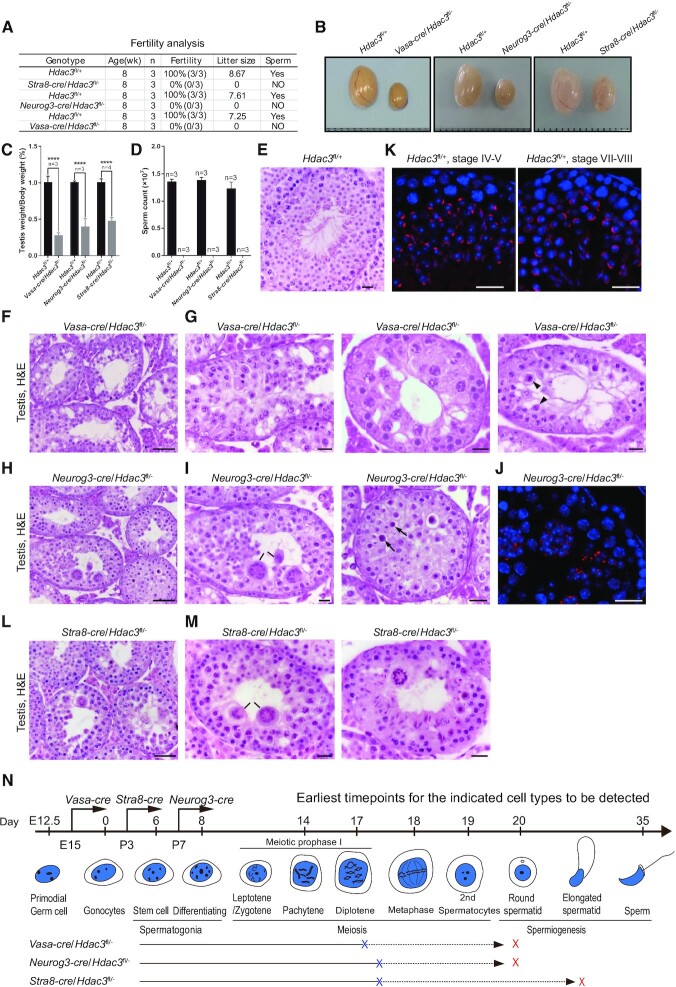
Figure 2.
Hdac3-deficiency causes male sterility and germ cell arrest at the late stages of prophase I and early RS stage. (A) Fertility data collected from adult Vasa-cre, Neurog3-cre, and Stra8-cre/Hdac3fl/– mice. n = 3 for each genotype. (B) Representative images of testes from adult Vasa-cre, Neurog3-cre, and Stra8-cre/Hdac3fl/– mice and their age-matched wild-types. (C) Testes weights were dramatically reduced in Vasa-cre, Neurog3-cre, and Stra8-cre/Hdac3fl/– mice at 8-week-old. Data presented is the ratio of testes weight and body weight (n = 3, *** P < 0.001, Student's t test). (D) Comparison of epididymal sperm counts between adult Vasa-cre, Neurog3-cre and Stra8-cre/Hdac3fl/– mice and their age-matched wild types. n = 3 for each genotype. *** P < 0.001, Student's t test. (E–I, L–M) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of testes from adult wild type (E), Vasa-cre/Hdac3fl/– (F, G), Neurog3-cre/Hdac3fl/– (H, I) and Stra8-cre/Hdac3fl/– (L, M). Arrowheads in (G) point to metaphase cells with apoptosis in stage XII tubules of Vasa-cre/Hdac3fl/–. Black lines in Figure 2I and M point to multinucleated cell clusters of round spermatids. Arrows in Figure 2I indicate apoptotic cells during the transition from metaphase cells into secondary spermatocytes in stage XII tubules of Neurog3-cre/Hdac3fl/–. (J, K) Immunofluorescent staining of PNA on testis sections from wild type (K) and Neurog3-cre/Hdac3fl/– (J). PNA is the acrosome marker, and acrosome formation at developmental step 4 and step 8 was showed in wild-type (K), but acrosome beyond step 2–3 was completely absent in Neurog3-cre/Hdac3fl/– males (J). Scale bars, 20 μm. (N) A diagram representing arrested stages of germ cell development in Vasa-cre, Neurog3-cre and Stra8-cre/Hdac3fl/– mice. Blue and red crosses on lines indicate the earliest and ultimate time point of spermatogenic arrest, respectively.