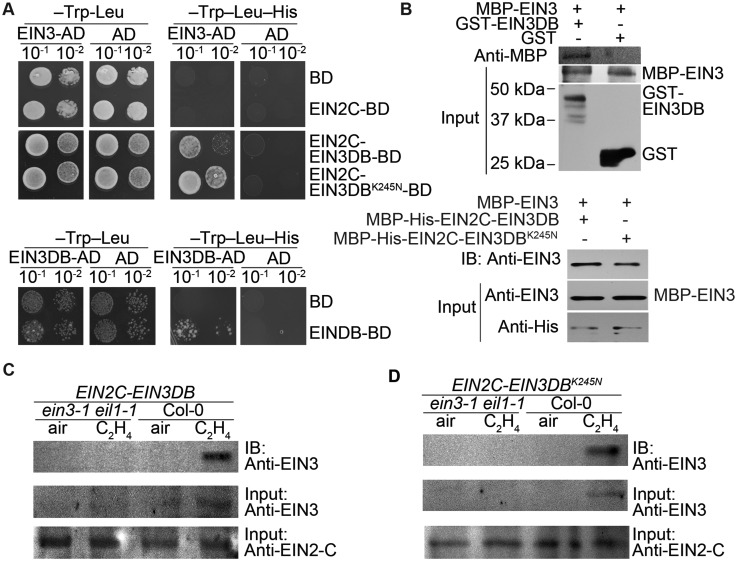
Figure 4.
EIN3 interacts with EIN2C–EIN3DB to regulate its binding activity. (A) Yeast two-hybrid assays to examine the interaction between EIN3 and EIN2C–EIN3DB (upper panel), and the dimerization of EIN3DB (lower panel). Yeast cells co-expressing the indicated combinations of constructs were grown on nonselective (left) or selective (right) medium. Different dilutions of cultures indicated in the figure were inoculated on each spot. (B) Pull-down assays to examine the interaction between EIN3 and EIN3DB, EIN2C–EIN3DB, or EIN2C–EIN3DBK245N. Reactions were performed using recombinant MBP-EIN3, GST-EIN3DB, and MBP-His fusion proteins (MBP-His-EIN2C-EIN3DB and MBP-His-EIN2C-EIN3DBK245N). Proteins were separated by SDS–PAGE and detected with anti-EIN3 or anti-MBP antibody. (C and D) In vivo immunoprecipitation assay to examine the interaction between EIN3 and (C) EIN2C–EIN3DB or (D) EIN2C–EIN3DBK245N in total protein extracts from 3-day-old etiolated seedlings of the indicated genotypes treated with or without ethylene.