Figure 7.
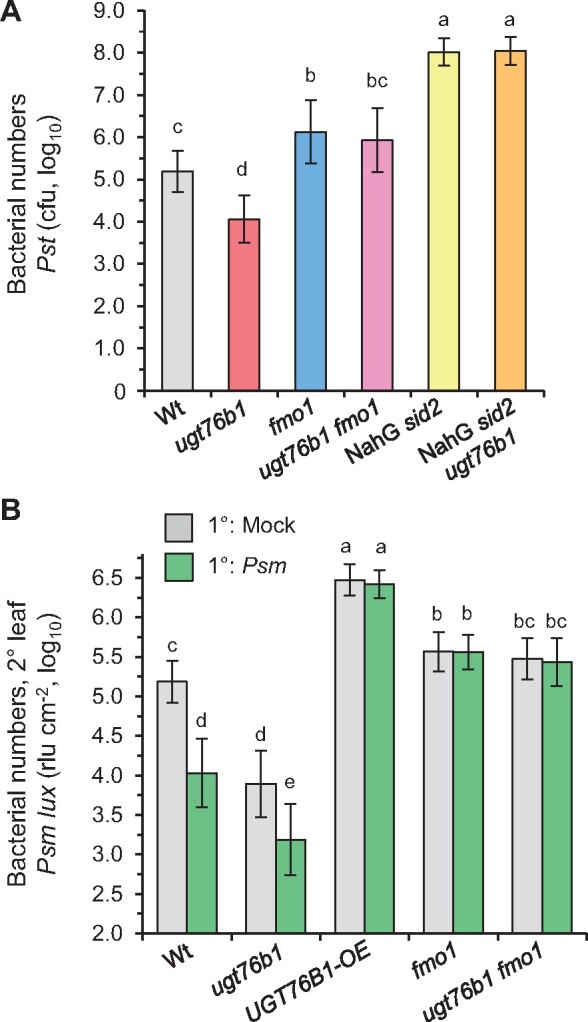
Local and systemic immunity is enhanced by ugt76b1 loss-of-function, whereas overexpression of UGT76B1 compromises SAR. A, Susceptibility of ugt76b1 introgressed into fmo1 and NahG sid2 toward Pst DC3000. Four-week-old Wt, ugt76b1, fmo1, fmo1 ugt76b1, NahG sid2, and NahG sid2 ugt76b1 plants were infiltrated with 5 × 104 cfu (OD600 = 0.0001) of Pst DC3000. Bacterial growth was monitored after 72 h. Bars are means ± sd of 15 replicates from three independent experiments, each experiment consisting of five biological replicates. The presented values are log10-transformed. Different letters denote significant differences (P < 0.01, ANOVA and post hoc Tukey HSD test). The smaller growth of ugt76b1 in comparison to Wt is ameliorated by the introgression of fmo1 or NahG sid2 (Supplemental Figure S10). B, The ugt76b1 mutant is able to induce SAR, whereas the UGT76B1-OE line is deficient in SAR. To assess SAR, three 1° leaves of a plant were mock-treated or Psm-inoculated (OD600 = 0.005). Two days later, three 2° leaves were challenge-infected with a bioluminescent Psm strain (Psm lux; OD600 = 0.001), and growth of Psm lux was assessed after 2.5 days by luminescence measurements. Bacterial numbers were determined as rlus per leaf area (rlu cm−2). The presented values are log10-transformed. Bars are the mean ± sd of 12 or more replicate leaf samples from 6 to 7 different plants. Different letters denote significant differences (P < 0.01, ANOVA and post hoc Tukey HSD test). Independent experiments yielded similar results with some variability of the SAR phenotype of ugt76b1 (Supplemental Figure S11).
