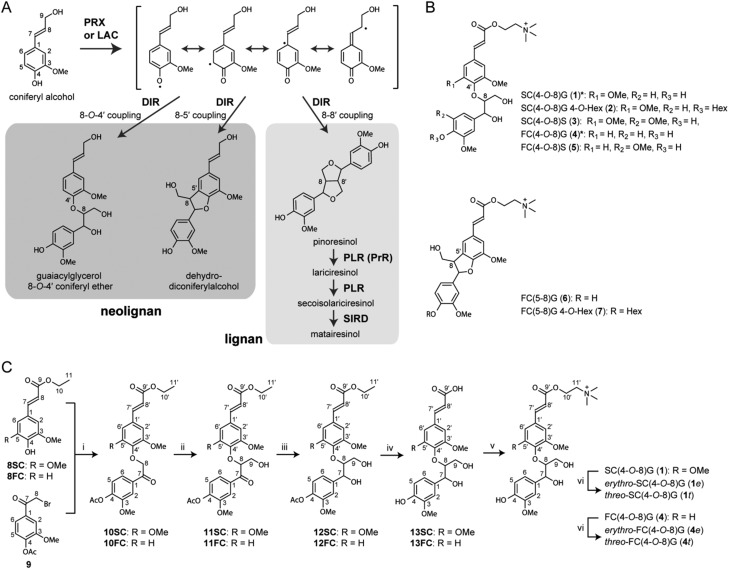
Figure 1.
Lignans and neolignans. (A) The biosynthetic pathways of lignans and neolignans. DIR, dirigent protein; LAC, laccase; PLR, pinoresinol/lariciresinol reductase; PrR, pinoresinol reductase; PRX, peroxidase; SIRD, secoisolariciresinol dehydrogenase. (B) Structures of neolignans in Arabidopsis seeds (see also Supplemental Table 1). G, Guaiacyl moiety; S, Syringyl moiety; SC, sinapoylcholine; FC, feruloylcholine; Hex, hexose. Asterisks indicate the compounds authenticated with chemically synthesized standards. (C) Synthetic scheme for neolignans SC(4-O-8)G (1) and FC(4-O-8)G (4). Reaction conditions: (i) acetone/K2CO3/reflux; (ii) dioxane/K2CO3/formaldehyde/r.t.; (iii) ethanol/NaBH4/r.t.; (iv) NaOH aq./r.t.; (v) DMF/bromocholine bromide/NaOH/90°C; (vi) preparative HPLC. r.t., room temperature.