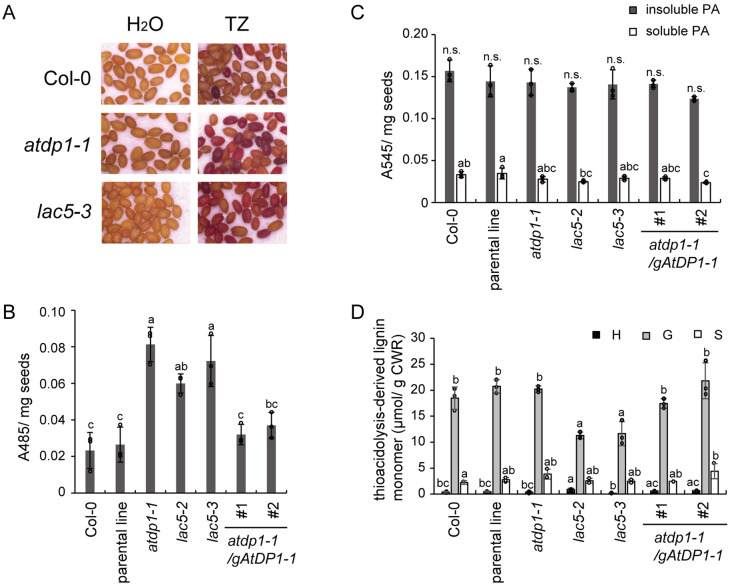
Figure 13.
Seed coat permeability of atdp1 and lac5 mutants. Seed coat permeability was tested by measuring the conversion of tetrazolium salts to red products called formazans. (A) Seeds of wild type (Col-0) and the mutants (atdp1-1 and lac5-3) stained in a tetrazolium salt (TZ) solution or H2O after 48 h incubation. (B) The absorbance of ethanol extracts containing formazan from the seeds stained with tetrazolium salts at 485 nm. The intensity of A485 is directly proportional to the permeability of the seed coat. (C) Soluble and insoluble proanthocyanidins were analyzed by acid hydrolysis as described in Materials and methods section. No significant difference (P < 0.05) was detected for the insoluble proanthocyanidins. (D) The yield of thioacidolysis-derived p-hydroxyphenyl (H)-, guaiacyl (G)-, and syringyl (S)-type trithioethylpropane monomers released from H-, G-, and S-type lignin polymer units. Data represent the means ± sd (three biological replicates per sample). The means were compared by a one-way ANOVA. Statistically significant differences (P < 0.05) were identified by Tukey’s test and are indicated by lowercase letters to represent differences between groups. n.s., not significant; CWR, cell wall residue.