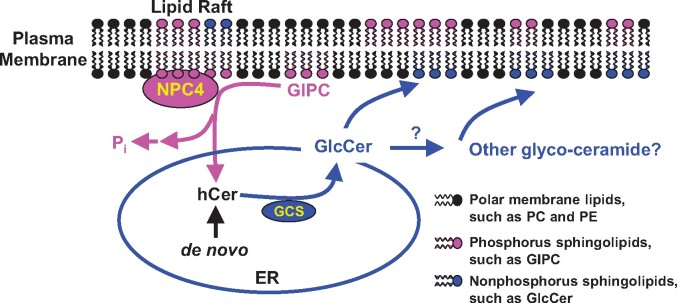
Figure 6.
Proposed model of sphingolipid hydrolysis by NPC4 in Arabidopsis roots in response to phosphate-deficiency. When phosphate is limiting, the expression of NPC4 increases and resulting NPC4 is associated mostly with the PM rafts in which GIPC is enriched. NPC4 hydrolyzes GIPC to release phosphate for other essential cellular processes. The hydrolysis of GIPC produces hCer, which serves as substrate for the synthesis of GlcCer that can be further glycosylated to produce other glycosyleramides. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; GCS, glucosylceramide synthase; GlcCer, glucosylceramide; GIPC, glycosyl inositol phosphoryl ceramide; hCer, hydroxyceramide; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; Pi, inorganic phosphate; PM, plasma membrane.