FIGURE 1.
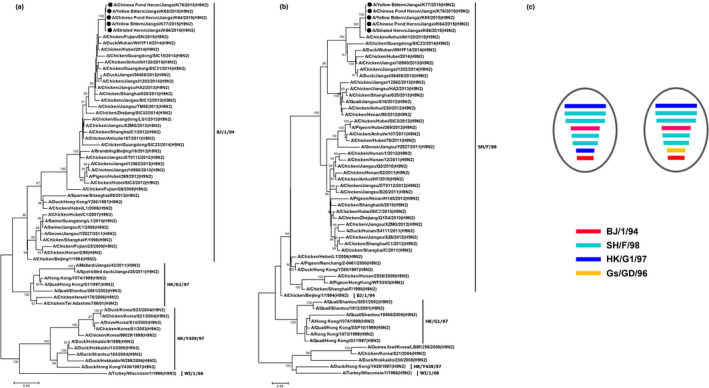
Phylogenetic analysis of five viruses isolated in Jiangxi, China in 2015. Molecular phylogenetic analyses for the (a) HA, (b) NA were conducted using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the Kimura 2‐parameter model. Viruses sequenced in this study were marked by circles. Internal branching probabilities were determined by bootstrap analysis with 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Viruses formed distinct groups, that is A/chicken/Beijing/1/94(H9N2) (BJ/1/94), A/chicken/Shanghai/F/98(H9N2) (SH/F/98), A/quail/Hongkong/G1/97(H9N2) (HK/G1/97) and A/goose/Guangdong/1/96(H5N1) (Gs/GD/96). (c) A hypothetical reassortment pattern of the novel H9N2 virus isolates. The eight gene segments (horizontal bars), that is PB2, PB1, PA, HA, NP, NA, M and NS, were ordered from top to bottom in each virion. Different colours represented different virus lineages
