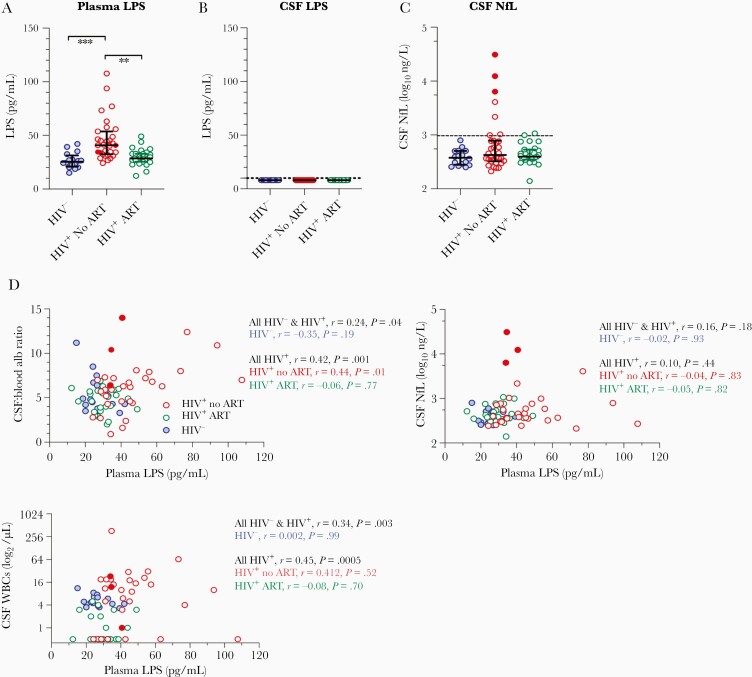
Figure 1.
Increased plasma level of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in human immunodeficiency virus–infected (HIV+) individuals and its direct correlations with the magnitude of blood-brain barrier permeability, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of neopterin, and white blood cell (WBC) counts. A, Increased plasma level of LPS was found in HIV+ individuals even after adjusting for age compared to controls. **P < .01, ***P < .0001. B, Central nervous system LPS was undetectable in all samples. C, CSF levels of age-adjusted neurofilament light chain (NfL). Three HIV+ individuals with dementia are shown in filled red circles. D, Correlations between plasma LPS and albumin ratio in CSF vs serum, CSF age-adjusted NfL level, and CSF WBC counts in HIV-negative controls and HIV+ individuals. Abbreviations: alb, albumin; ART, antiretroviral therapy; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NfL, neurofilament light chain; WBC, white blood cell.