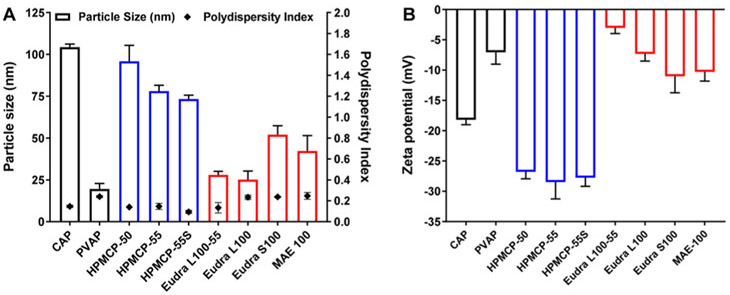
Figure 3.
Characterization of polycarboxylate nanoparticles (NPs): (A) particle size and polydispersity index and (B) surface charge or zeta potential of polycarboxylate NPs. The size of the polycarboxylate NPs was dependent on the type of polycarboxylate polymer. The polydispersity index values were <0.3 for all nanoformulations, indicating uniformity of NPs. All polycarboxylate NPs showed a negative zeta potential value due to the presence of the carboxylate end groups (data expressed as mean ± S.D.; n = 3). CAP: Cellulose acetate phthalate; PVAP: polyvinyl acetate phthalate; HPMCP: hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate; Eudra: Eudragit; MAE 100: Kollicoat MAE 100P.