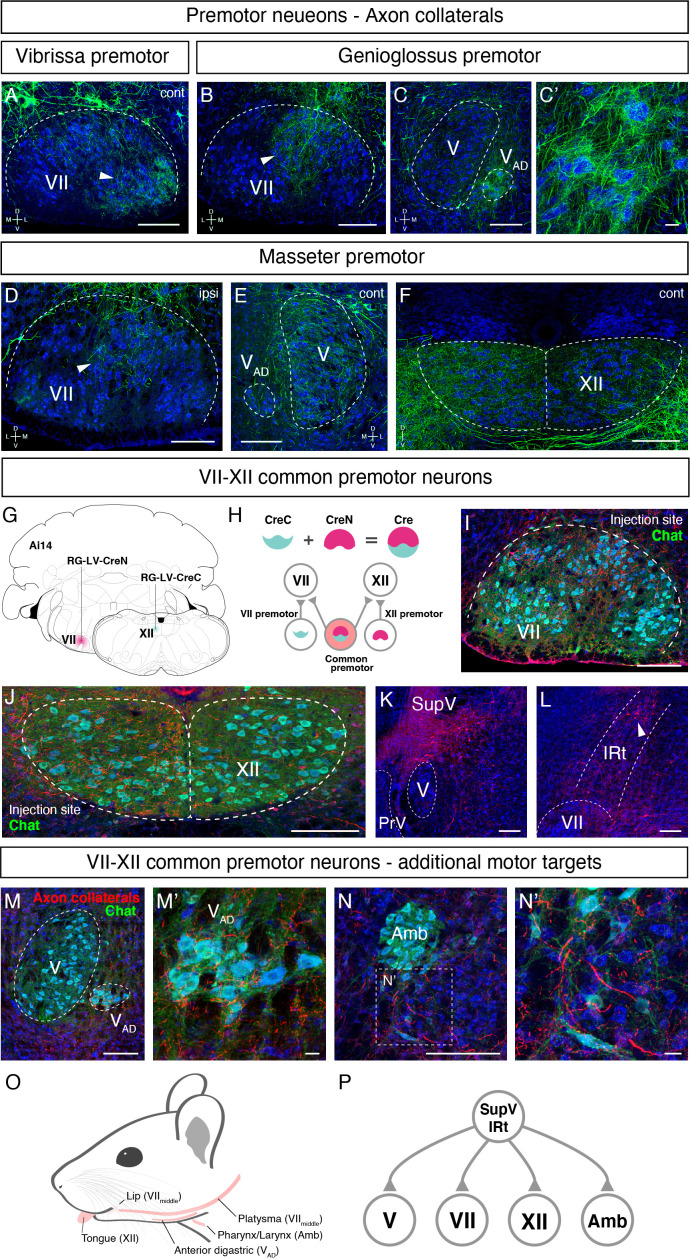
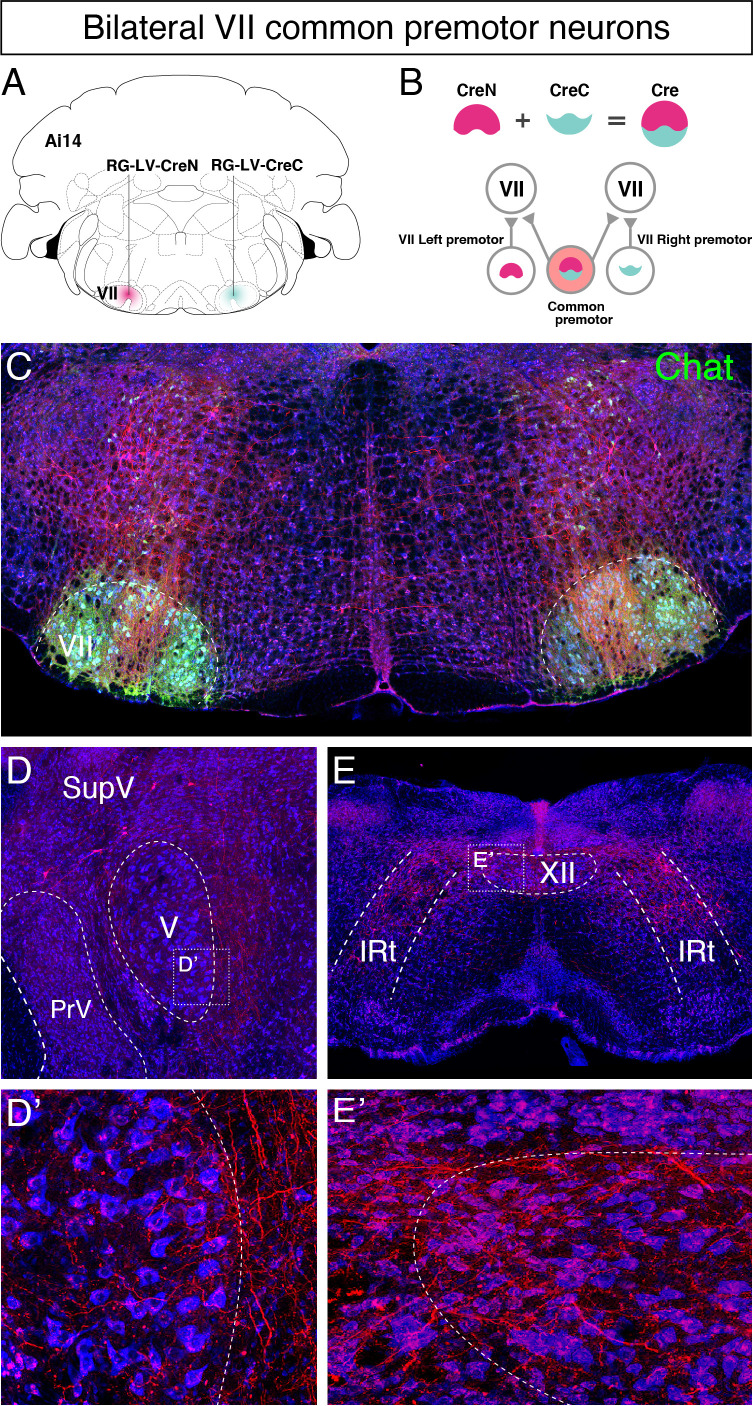
Figure 7. Common premotor neurons innervate multiple distinct orofacial motor nuclei.
(A–F) Representative images of axon collaterals from rabies labeled premotor neurons traced from one muscle innervating other orofacial motor nuclei. Sections were counterstained with fluorescent Nissl (blue). (A) Axon collaterals from ipsilateral vibrissa premotor neurons innervate the contralateral vibrissa motoneurons in the lateral part of VII (arrowhead). (B–C') Axon collaterals of some genioglossus premotor neurons also innervate the middle part of VIImiddle (arrowhead, B) and innervate the anterior digastric part of V (VAD) (C, magnified view is shown in C'). (D–F) Axon collaterals from masseter premotor neurons also innervate the middle part of VIImiddle (D), the contralateral V (E), and the dorsal part of XII (F). (G–P) Identifying VIImiddle-XII common premotor neurons. (G, H) Schematic of split-Cre tracing strategy. (G) RG-LV-CreN and RG-LV-CreC were injected into the left side of VIImiddle and XII of Ai 14 mice, respectively. (H) Cre is reconstituted only in neurons innervating both VIImiddle and XII, and which induces tdTomato reporter expression. (I, J) Representative images of axons/axon collaterals in the injection sites. Sections were counterstained with fluorescent Nissl (blue). Motoneurons were stained with anti-chat antibody (green). VII (I). XII (J). (K, L) Representative images of VIImiddle-XII common premotor neurons in supratrigeminal region (SupV) (K) and the dorsal intermediatereticular nucleus (IRt) (L). (M–N') Representative images of axon collaterals from VIImiddle-XII common premotor neurons in VAD (M, magnified view is shown in M') and Amb (N, magnified view is shown in N'). Scale bars, 200 µm (A–F, I–N); 20 µm (C', M', N'). (O) Schematic showing orofacial muscle targets of motor nuclei. (P) Schematic of all motor nuclei innervated by VIImiddle-XII common premotor neuron in SupV and IRt.