Figure 3. Effect of smoking metrics on mutations and TMB.
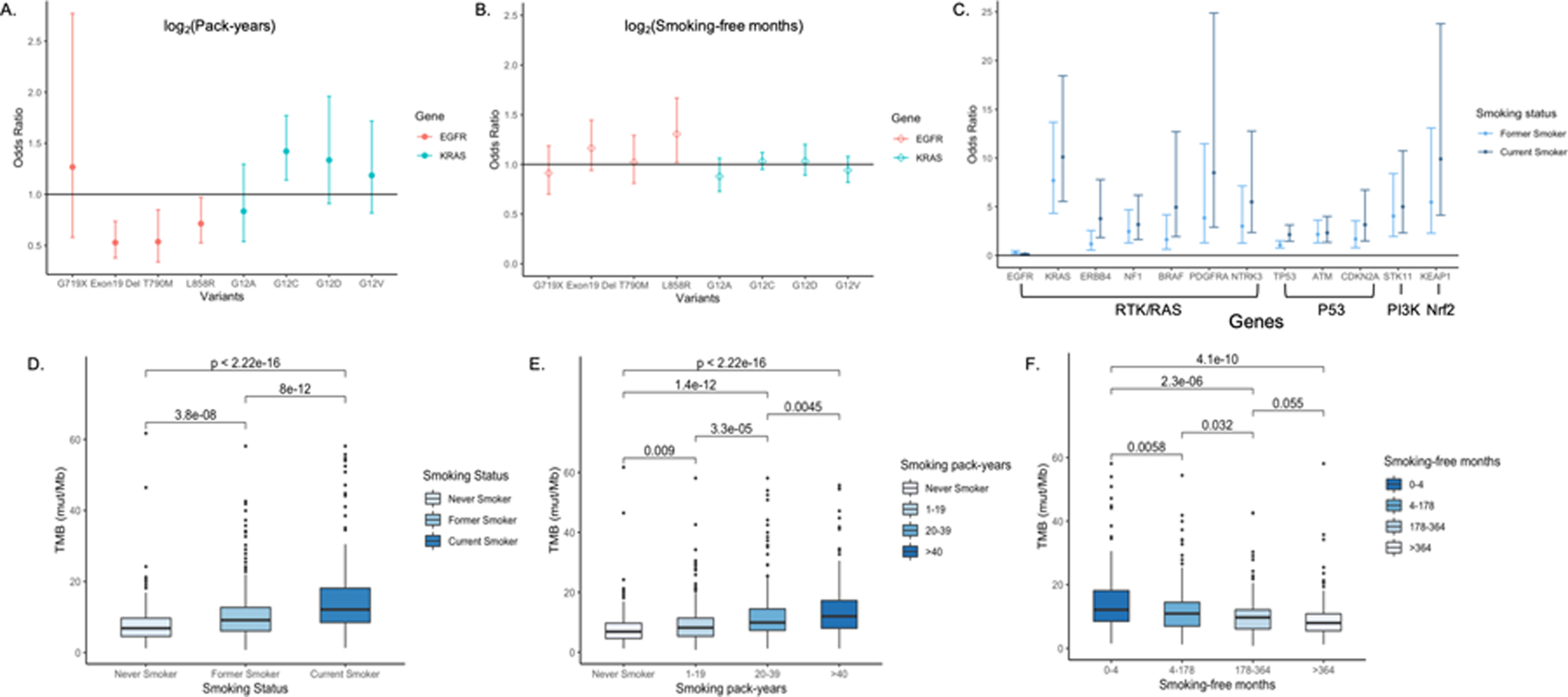
A. Odds ratios of EGFR and KRAS variant-specific mutations for smoking pack-years. B. Odds ratios of EGFR and KRAS variant-specific mutations for smoking-free months. C. Odds ratios of somatic mutations in cancer related pathways for former and current smokers obtained from multivariable logistic regression controlling for age, gender, stage and histological subtypes. D. TMB is significantly associated with smoking status, with the highest median TMB observed in current smokers (12.1 mut/Mb), followed by former and never smokers (9.1 mut/Mb and 6.8 mut/Mb, respectively). E. All patients were divided into never smokers and ever smokers and smoking pack-years in ever smokers were divided into tertiles. Smoking pack-years are significantly associated with TMB. F. Ever smokers were divided based on quartiles of smoking-free months. Smoking-free months are significantly associated with TMB. Pairwise comparisons by Wilcoxon test were conducted and FDR adjusted p-values are labeled. P ≤ 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
