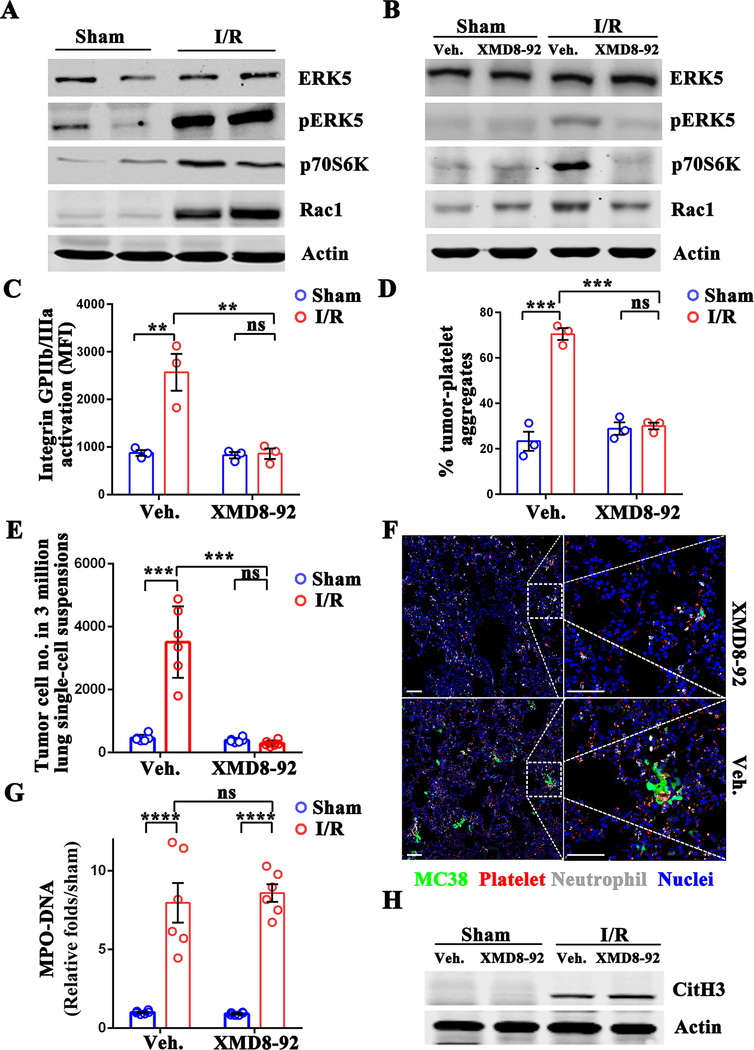
Figure 5.
Aggregation of platelets and CTCs under hepatic I/R stress is platelet ERK5-dependent. (A) Western blot analysis of ERK5, pERK5, p70S6K, and Rac1 proteins in platelets following 1.5 hours of hepatic ischemia and 3 hours of reperfusion. (B) Mice were given intraperitoneal injections of XMD8–92 (50 mg/kg) 6 hours prior to hepatic I/R. Protein levels in platelets 3 hours post I/R were determined by western blot. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of integrin activation in platelets extracted from XMD8–92 or vehicle-treated mice following sham laparotomy or hepatic I/R. (D) Aggregation capacity of platelets from C with MC38 cells. (E) FACS quantitative data of MC38 cell numbers in the lungs of XMD8–92 or vehicle-treated mice 12 hours after tumor cell injection. (F) Representative immunofluorescence images showing tumor cells arrested at 24 hours following hepatic I/R in XMD8–92 or vehicle-treated mice. Green: MC-38; Red: Platelet; Grey: Neutrophil; Blue: Nuclei. Scale bar, 100μm. (G) Serum MPO-DNA complex levels were assessed in XMD8–92 or vehicle-treated mice following sham laparotomy or 1.5 hours of ischemia and 6 hours of reperfusion. (H) The level of Cit-H3 protein was determined by western blot analysis in XMD8–92 or vehicle-treated mice in G. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from n = 3–6 mice per group. ns: not significant, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001.