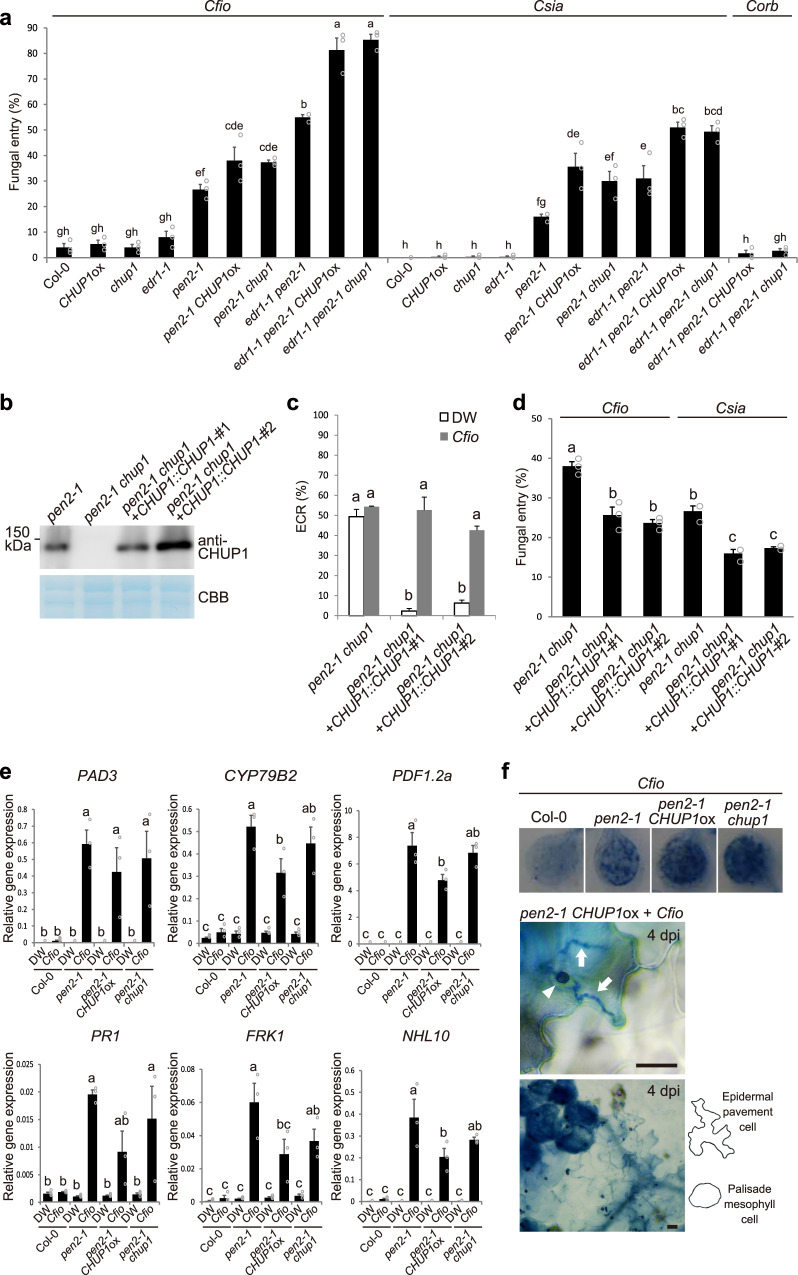
Fig. 4. The ECR contributes to Arabidopsis NHR against Colletotrichum fungi.
a Fungal entry rate into the epidermis of ECR-defective Arabidopsis. A total of 100 melanized appressoria were examined at 4 dpi. b CHUP1 protein levels in the indicated plants. Protein extracts were analyzed by immunoblot with anti-CHUP1 antibody. CBB staining was used as a loading control. c ECR of pen2-1 chup1 and CHUP1-complementation lines. A total of 100 cells in contact with the melanized appressorium were examined at 2 dpi. DW was used as a control. d Entry rate of Cfio and Csia into the epidermis of pen2-1 chup1 and CHUP1-complementation lines at 4 dpi. e Induced gene expression of PAD3, CYP79B2, PDF1.2a, PR1, FRK1, and NHL10 by inoculation of Cfio. Cfio was inoculated onto cotyledons of the indicated Arabidopsis. Gene expression was assayed at 24 hpi by RT-qPCR. DW was used as a control. f Epidermal and mesophyll cell death caused by appressorium-mediated entry of Cfio at 4 dpi. The inoculated plants were subjected to TB staining and observed macroscopically (upper) and microscopically using x40 (middle) and x10 (lower) objective lenses. The arrowhead and arrows indicate melanized appressorium and invasive hyphae, respectively. Scale bar, 20 µm. For all quantification analyses except RT-qPCR, the means and SE were calculated from three independent plants. The means and SE of RT-qPCR results were calculated from three independent experiments. Means not sharing the same letter are significantly different (P < 0.05, two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test).