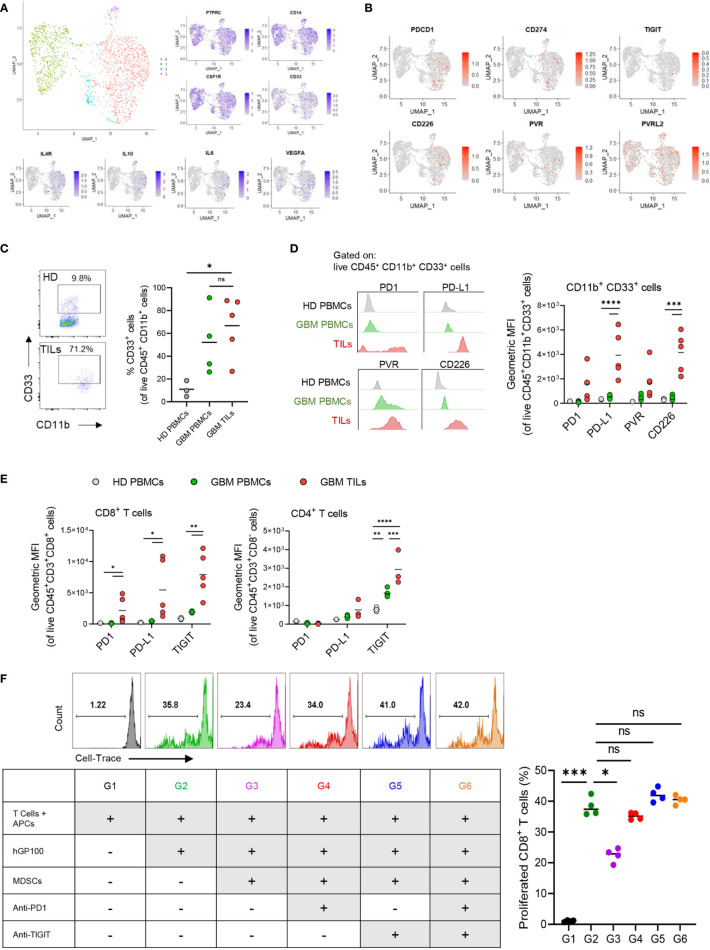
Figure 6.
PD1, PD-L1 and TIGIT-ligands are expressed on myeloid suppressor cells in GBM and contribute to T cell dysfunction. Single cell (sc) RNA-seq analysis was performed on myeloid cells from GBM patients. (A) UMAP clustering and expression (z-scores) of suppressive myeloid cell markers. (B) Expression z-scores of PD1/TIGIT-associated checkpoint molecules in the scRNA-seq clusters. (C–E) Healthy donor (HD) PBMCs and GBM patient PBMCs and TILs analyzed flow cytometry for myeloid cells, T cells, and IC markers. n = 4 HD; n = 5 GBM patients. (C) Representative flow cytometry plots and percentages (%) of CD11b+ CD33+ myeloid cells. (D) Representative histograms and mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of PD1, PD-L1, PVR, and CD226 on CD11b+ CD33+ cells. (E) MFI of PD1, PD-L1, PVR, and CD226 on CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells. (F) T cell proliferation assay of murine hGP100-reactive CD8+ T cells cultured with immunosuppressive myeloid cells with αTIGIT and αPD1. Representative histogram plots and percentages (%) of proliferated CD8+ T cells at different culture conditions as indicated in the table lagend. n=4 per group. One-way ANOVA with Tukey multiple comparisons correction. ns, not significant. p = *<0.05, **<0.01, ***<0.001, ****<0.0001.