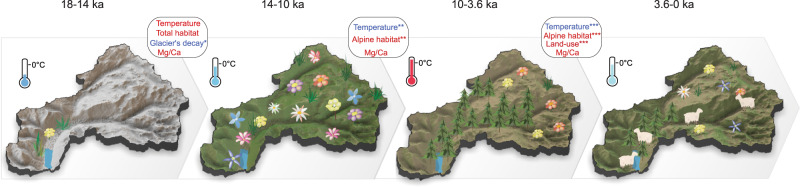
Fig. 4. Visualization of total plant taxa richness and effects of abiotic factors on plant richness across four time-intervals.
We calculated the statistical relationship between total plant richness and predictor variables (rounded rectangle) between consecutive periods of time (Methods). Alpha significance codes of Spearman correlation are ***0.0005, **0.01, and *0.025 according to adjusted degrees of freedom. The mean annual temperature anomaly is indicated by the thermometer. Positive and negative correlation is marked in red and blue font, respectively. The catchment sketches illustrate that disturbance in the glaciated landscape was likely of importance during the deglaciation period. Our results indicate that once the catchment became ice-free, alpine habitat extent is the main driver of total plant richness while land-use is only of secondary importance during the late Holocene. From the switch in correlation sign, we assume that temperature is likely not a direct driver of richness change.