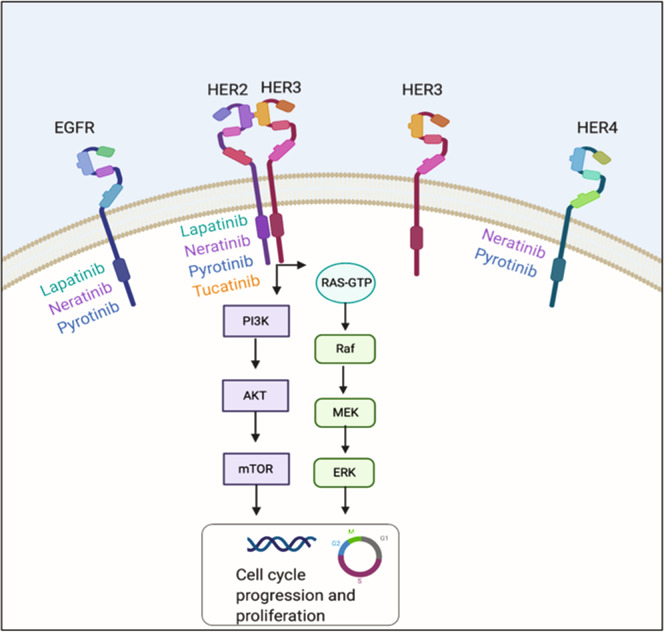
Fig. 1. Mechanism of action of HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
There are four members of the HER2 receptor family, these are the targets of lapatinib, neratinib, pyrotinib and tucatinib. The HER2 extracellular domain has no known ligand and is activated by the formation of homo or heterodimers (exemplified by a HER2-HER3 heterodimer in the figure). These dimers lead to phosphorylation of tyrosine kinase residues in the cytoplasmic domain which function as docking sites for proteins that activate the PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways downstream leading to cell cycle progression and proliferation.