Figure 2.
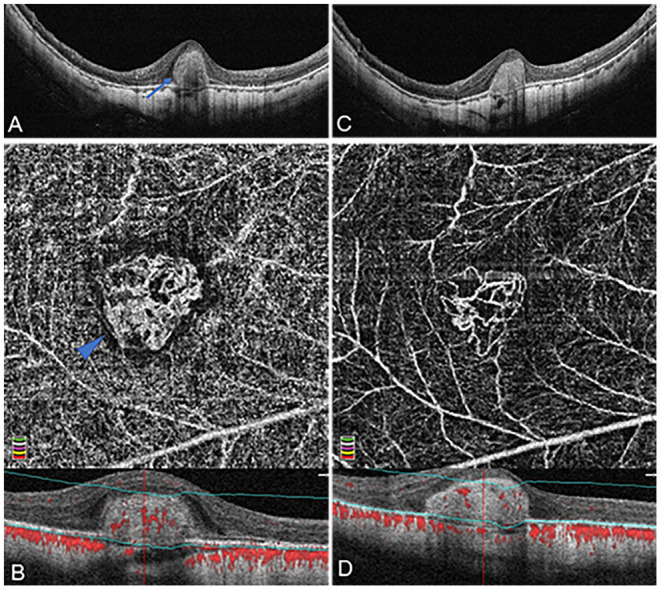
Organized interlacing pattern of active mCNV imaged by OCT and OCTA before and after anti-VEGF injection in Patient #15, a 49-year-old man (refractive error −14.75 diopters) in the right eye. OCTA segmentation was manually adjusted to acquire a clear en face image visualizing the entire thickness mCNV lesion. (A) Spectral-domain OCT B-scan at baseline showed a typical subretinal hyper-reflective type-2 CNV (blue arrow) with discontinuous retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). (B) OCTA en face image (3 × 3 mm) at baseline depicted a larger, well-circumscribed, interlacing type of neovascular membrane. This mCNV lesion contained numerous tiny capillary ramifications, anastomoses and loops, which was bordered by a dark halo, showing a medusa shape (blue arrowhead). (C) One month after the first injection, OCT image revealed significant shrinkage of CNV lesion with a clearer contour. (D) One month after the first injection, OCTA en face image (3 × 3 mm) indicated a reduction of CNV size, anastomoses, and perilesional halo, a dramatic attenuation of capillaries and small caliber vessels, and a reservation of large caliber vessels. The lower parts of image (B,D) represented the cross-sectional structural OCT images corresponding to the upper OCTA en face images, respectively, displaying the boundaries (green lines) of the OCTA slabs after manual adjustment of segmentation.
