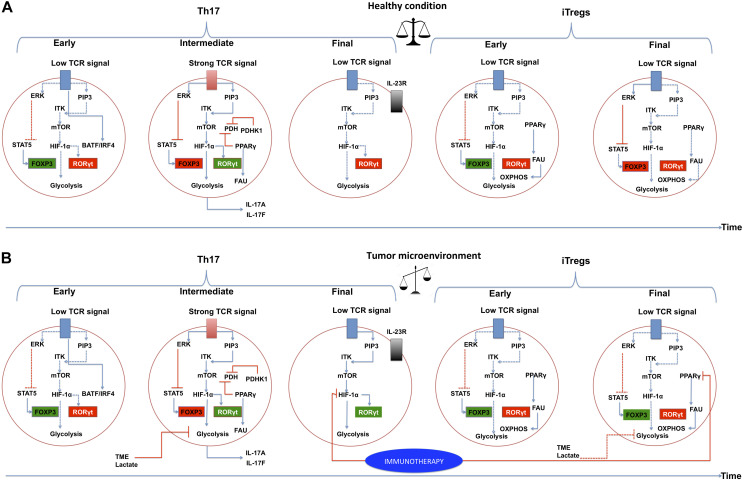
FIGURE 4.
The PI3K–AKT–mTOR pathway and metabolic programs converge to regulate the differentiation of inflammatory versus regulatory T cells in a tumor microenvironment. Links between extracellular cues, T-cell receptor (TCR) strength, the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)–AKT–mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway, metabolic programs and gene regulation are depicted. (A) Normal conditions. Three stages of differentiation over time are shown for Th17, at the end of the timeline, Tregs differentiation is presented to indicate that these require more time to differentiate. IL-2-inducible T-cell kinase (ITK) and TCR signaling play a critical role in regulating the expression of transcription factor hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α) by functioning as a rheostat that determines the extent of activation of PI3K and mTOR-activated pathways. HIF-1α is activated in intermediate and deactivated in final steps of Th17 differentiation. A balance between Th17 cells and Tregs is achieved and they can co-exist in the time. PPARγ in Tregs should be deactivated in a specific time. (B) Tumor microenvironment conditions. We suggest a deregulation of the signaling pathways in Th17 cells and Tregs. It is likely that HIF-1α is not inactivated in a tumor microenvironment, leading to a higher expression of RORγt, and generating an exhausted Th17. Likewise, PPARγ may not be deactivated in Tregs, leading to functional Tregs. Immunotherapy proposals could be directed at targets such as HIF-1α and PPARγ. Activated interactions between components are indicated by solid lines, whereas inactivated links between proteins are denoted with dashed lines. The blue lines indicate positive direct interactions between the components. Red lines indicate direct negative interactions. The green squares indicate that the component is active, the red square indicates that the component is inactive. ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase pathway; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; STAT5, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5; FOXP3, forkhead box P3; RORγt, RAR-related orphan receptor gamma; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; PDHK1, pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; FAU, fatty acid uptake; TME, tumor microenvironment.