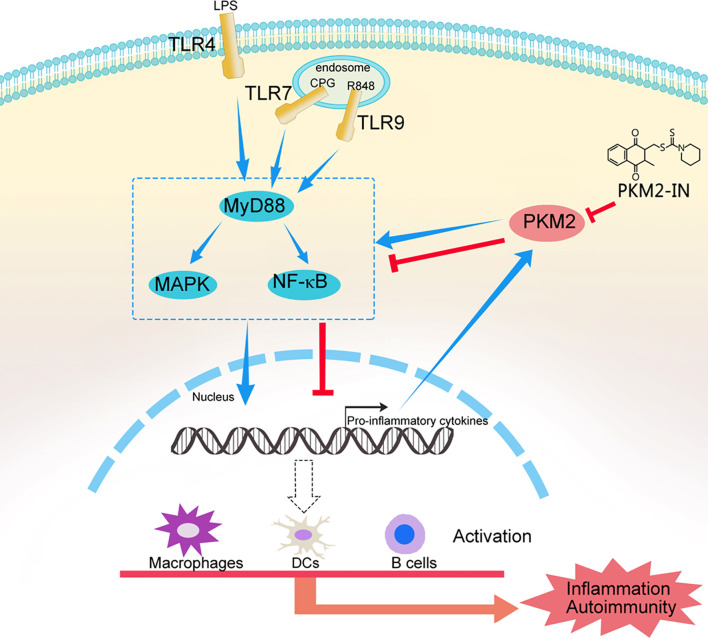
Figure 10.
A model of the mechanism whereby PKM2 participates in the pathogenesis of TLRs-mediated inflammation and autoimmunity. This schematic shows that hyper-activation of TLRs lead to PKM2 over-expression and PKM2 augments TLR4/TLR7/TLR9-induced activations of macrophages, DCs and B cells by promoting Pyk2 activation, thereby contributing to the pathogenesis of TLRs-mediated inflammation and autoimmunity. Pharmaceutical inhibition of PKM2 by PKM2-IN can inhibit TLR4/TLR7/TLR9-induced activations of macrophages, DCs and B cells, and alleviate the pathogenesis of TLRs-mediated inflammation and autoimmunity.