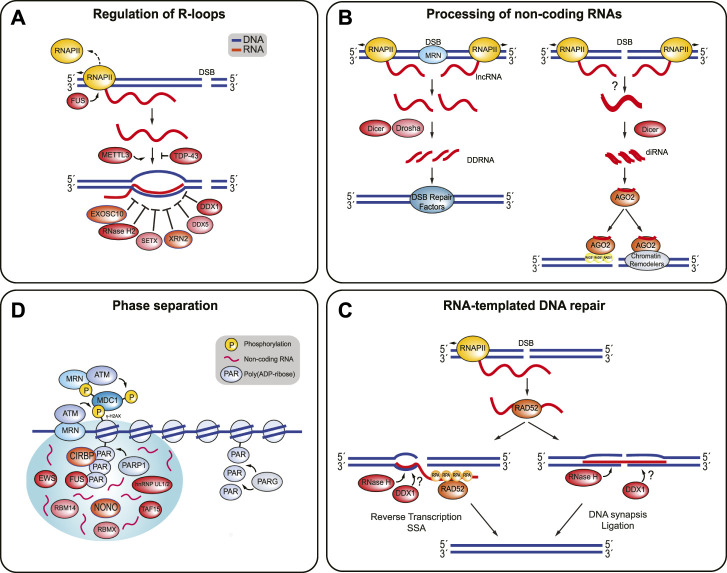
FIGURE 3.
RBPs involved in the regulation of R-loop structures, processing of non-coding RNAs, RNA-templated DNA repair, and phase separation. (A) The presence of R-loops at DSBs is highly regulated. FUS prevents R-loop formation by promoting RNAP II dissociation. TDP-43 prevents the nascent RNA from binding to DNA. METTL3 stabilizes these RNA:DNA hybrids. EXOSC10, RNase H2, SETX, XRN2, DDX5, and DDX1 are some of the RBPs involved in resolving RNA:DNA hybrids and R-loops. (B) Non-coding RNAs can be processed into DDRNAs or diRNAs. DDRNAs are produced when MRN complex induces production of dilncRNAs by recruiting RNAP II to both ends of the DSB break. The dilncRNAs can be processed by Drosha and Dicer into DDRNAs, which recruit DSB repair proteins to the DSB. In addition, diRNAs are created when RNA transcripts are synthesized near a DSB site by RNAP II become double-stranded and are processed by Dicer. It is unclear how the RNA becomes double-stranded in humans. The diRNAs are then incorporated into Argonaute-2 (AGO2) and AGO2 can then recruit RAD51. AGO2 also helps localize chromatin modifiers to the break site, which also promotes HR. (C) RNA-templated DSB repair begins with RAD52 binding to a ssRNA transcript and facilitating RNA:DNA hybrid formation. RAD52 can stimulate DNA recombination or end joining. DNA recombination is promoted when RAD52 undergoes inverse strand exchange, with help from RPA. Reverse transcription and SSA annealing completes the repair process. On the other hand, RAD52 promotes end joining by bridging both ends of the DSB with the homologous RNA transcript. DNA synapsis and ligation finish the repair. The RNA transcript is most likely removed from the DNA by RNase H enzymes and possibly DDX1. (D) PARP1 attaches poly (ADP-ribose) (PAR) chains to the DNA surrounding the DSB. Several RBPs are recruited to the DSB site in a PARP-1 dependent manner, where they may contribute promote phase separation around the break site. Non-coding RNAs are likely present and encourage phase separation. PARG disrupts phase separation and releases the RBPs by hydrolyzing the PAR chains.