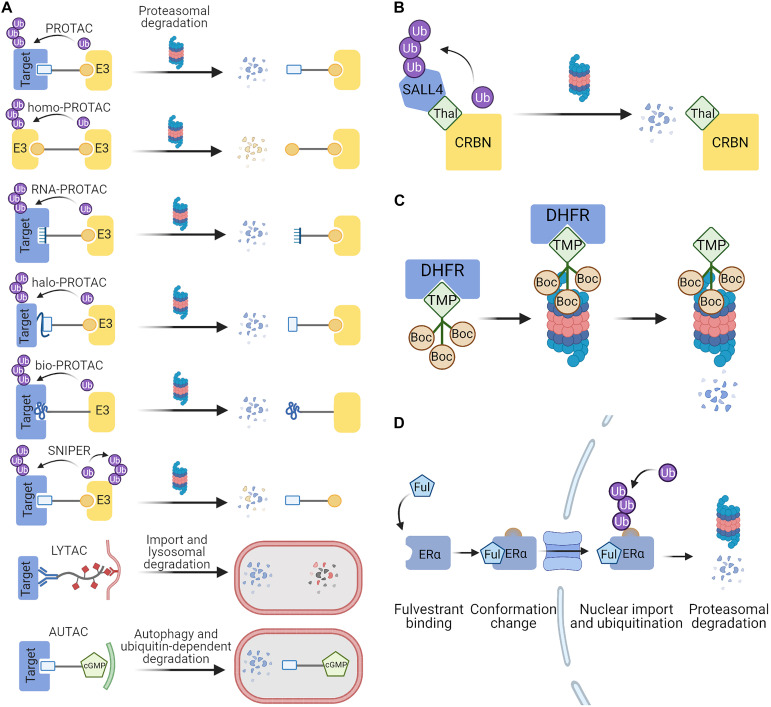
FIGURE 3.
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) strategies exploited in eukaryotes. (A) PROTACs are bifunctional chimeras which mediate the recruitment of an E3 ubiquitin ligase to the target protein. PROTAC components can be peptides, small molecules or oligonucleotides recognized as ligands by the target proteins. Ubiquitination of the target results in its degradation by the proteasome, while the PROTAC molecules are recycled for the next proteolytic event. LYTACs and AUTACs direct proteins for lysosomal degradation by promoting their encapsulation in endosomes and autophagosomes, respectively. (B) Thalidomide serves as a molecular glue which brings together SALL4 and the cereblon (CRBN) E3 ligase complex. SALL4 becomes a neo-substrate for the ubiquitination by CRBN and is then degraded by the proteasome (Yamanaka et al., 2020). (C) Hydrophobic tagging uses chimeric compounds in which a known protein ligand is linked to a highly hydrophobic Boc3-Arg, which is recognized as a degron by the proteasome. DHFR can be targeted for degradation through the use of its ligand trimethoprim in the chimeric hydrophobic tag (Shi et al., 2016). (D) Fulvestrant binding to the estrogen receptor α causes conformational changes which exposes the hydrophobic parts of the protein that serve as a degron. The Fulvestrant-bound ERα is degraded in the nucleus through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (Cornella-Taracido and Garcia-Echeverria, 2020). Figures were created with BioRender.com.