Fig. 1.
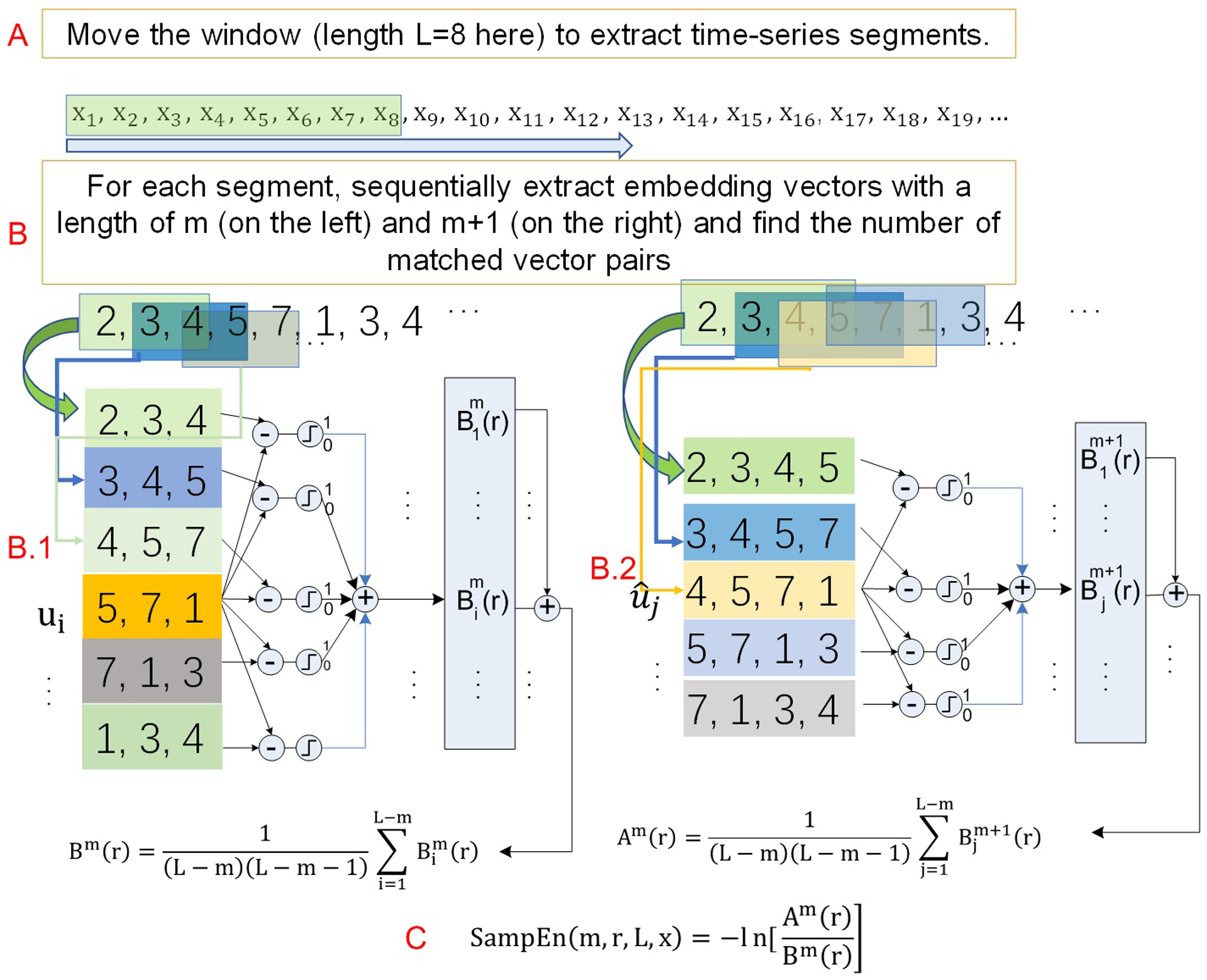
A scheme of the sliding window-based dynamic entropy calculation. A) A large time window is used to extract a sub-time series at N successive timepoints (N=8 here) from the original time series. The green box indicates the window slid to the n-th timepoint. B) The standard sample entropy formula is used to calculate entropy for the sub-time series extracted from A. B.1 and B.2 illustrate the embedding vector matching process for the embedding window length of m and m+1, respectively. The boxes in different color indicate the locations of the embedding vectors in the input time series—the sub-series from A).
