Figure 1.
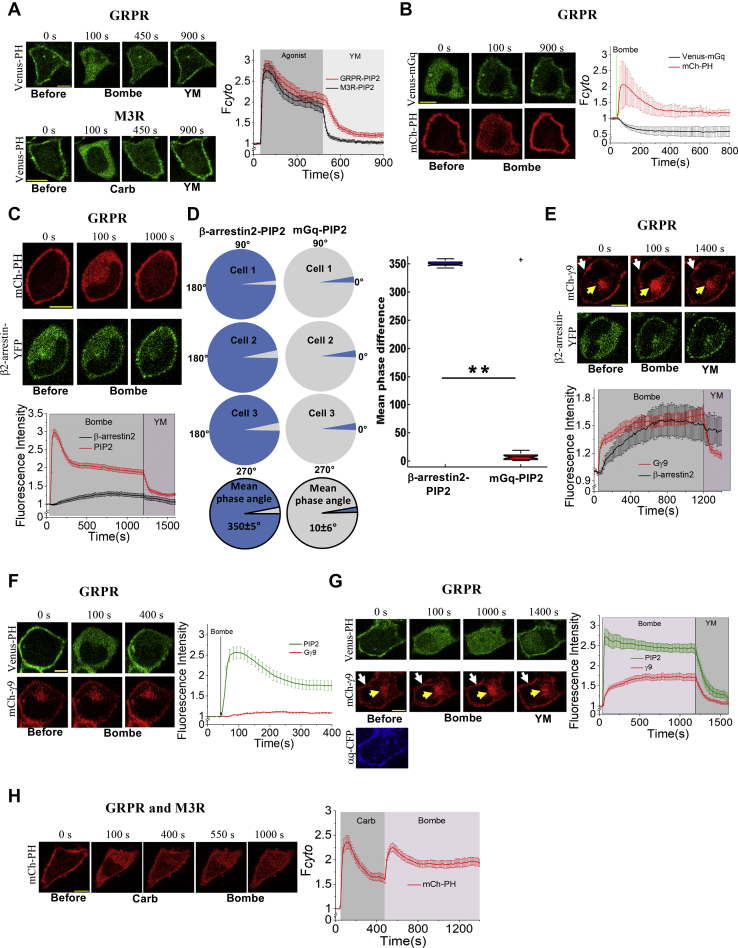
Gq-coupled GPCRs induce an efficient yet fast-attenuating PIP2 hydrolysis.A, HeLa cells exhibited efficient PIP2 hydrolysis and its attenuation upon activation of the GRPR (with 1 μM bombesin) and M3R (with 10 μM carbachol). The corresponding plot shows the magnitudes of the PIP2 sensor (Venus–PH) accumulation in the cytosol. B, HeLa cells expressing the GRPR, Venus–mGq, and mCh–PH exhibited mGq recruitment to PM upon addition of 1 μM bombesin. The mGq was retained on PM during PIP2 hydrolysis and its subsequent adaptation (PIP2 recovery). The corresponding plot shows the PIP2 and mGq dynamics in the cytosol of the cells. C, in an experiment similar to that in panel B, instead of mGq, b-arrestin2 recruitment to the PM was monitored. D, the mean phase difference obtained using Hilbert transform for depicting the correlation within the two time-series data (sample three cells) for b-arrestin2, PIP2 (blue), and mGq, PIP2 (red). The corresponding mean phase differences of all the cells within each pair of experimental data represented as box plots (ANOVA test: ∗∗p < 0.005, (+ represents outliers)). E, HeLa cells expressing Gαq–CFP, mCh–γ9, b-arrestin2–YFP, and GRPR showed characteristic Gγ9 translocation and b2-arrestin2 recruitment to the PM upon addition of 1 μM bombesin. F, activation of the GRPR in HeLa cells (1 mM bombesin) results in a minor Gg9 translocation that reached lasting plateau. Although Gg9 stayed translocated, the same cells showed the typical PIP2 hydrolysis and its partial adaptation. G, upon expressing aq-CFP, GRPR activation in HeLa cells induced a robust mCh–g9 translocation (compared with that in panel F). However, the PIP2 hydrolysis remained adaptation resistant. Upon Gq inhibition with YM-254890, Gg9 translocation reversed, whereas PIP2 completely recovered, reaching the preactivation conditions. H, HeLa cells expressing both M3R and GRPR first treated with 10 μM carbachol to induce PIP2 hydrolysis. After PIP2 partial recovery of PIP2 at the PM, the same HeLa cells treated with 1 μM bombesin showed rehydrolysis of the recovered PIP2. This hydrolysis also subsequently partially adapted. The plot shows the PIP2 sensor dynamic in the cytosol of the cells during basal and carbachol- and bombesin-stimulated states. Note: PM (white arrows) and IMs (yellow arrows). The scale bar represents 10 μm. Average curves plotted using n ≥10 cells from ≥3 independent experiments. The error bars represent the SEM. GRPRs, gastrin-releasing peptide receptors; IMs, internal membranes; M3R, M3-muscarinic receptor; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate.