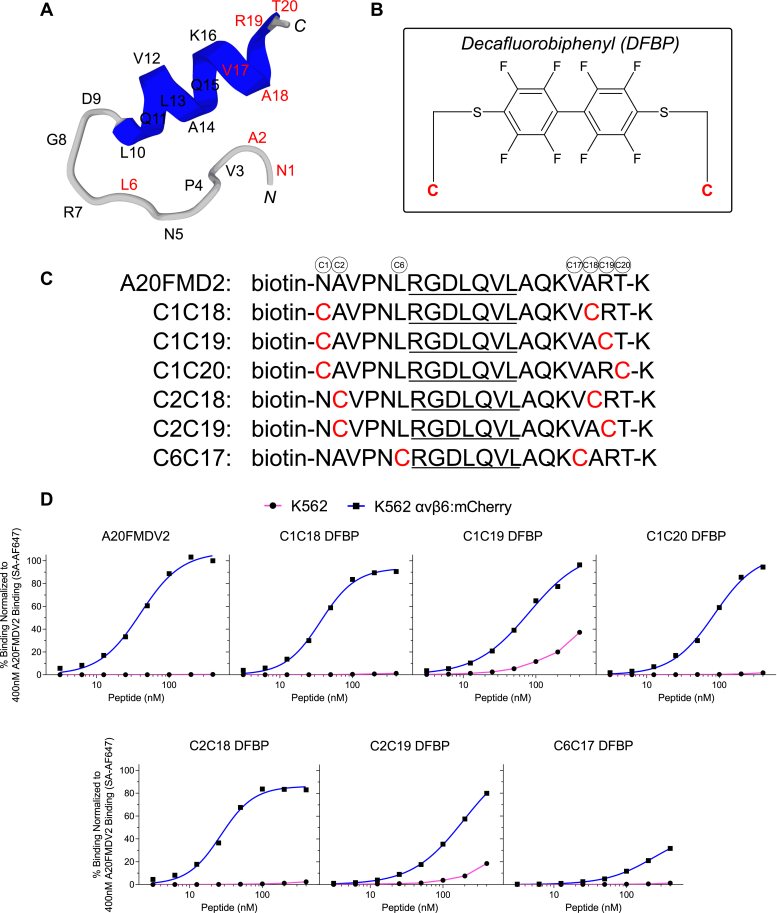
Figure 1.
Site-specific cyclization of A20FMDV2 via perfluoroarylation retains peptide binding to αvβ6+cancer cells.A, 3D model of A20FMDV2 peptide predicted by PEP-FOLD3 computational framework (68). Amino acids are listed, and positions substituted with cysteines for cyclization are shown in red. B, chemical structure of decafluorobiphenyl (DFBP) molecular linker used for cyclization. C, amino-acid sequences of A20FMDV2 peptide and DFBP-cyclized variants. Cysteine substitutions for cyclization by perfluoroarylation are shown in red. The RGDLXXL motif that is important for αvβ6 recognition is underlined in all sequences. D, flow cytometry binding curves of A20FMDV2 peptide and DFBP-cyclized variants to K562 and K562 αvβ6:mCherry cells, normalized to 400 nM A20FMDV2 binding to K562 αvβ6:mCherry cells. The curves represent a nonlinear regression of one independent experiment in which binding data are fitted to a Hill equation. KD values are not shown here and will be reported for promising peptides in a later figure with triplicate datasets. SA-AF647, streptavidin Alexa Fluor 647.