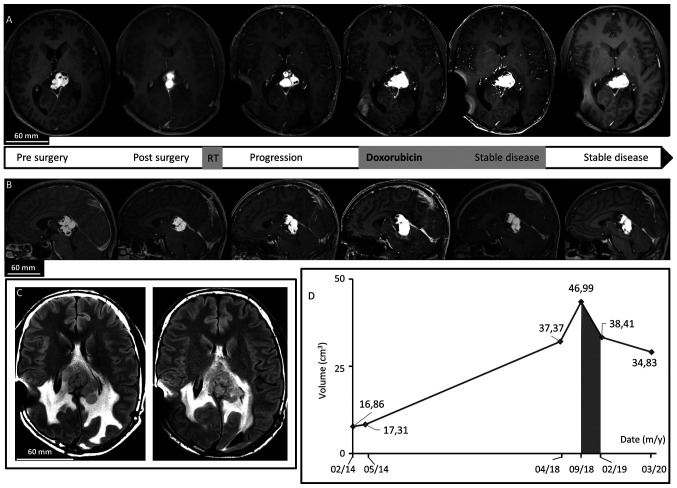
Figure 1.
Brain MRI. (A) Axial after gadolinium injection T1-weighted imaging revealed dominant, patchy intense enhancing lesion of the splenium of the corpus callosum and the pineal region. In chronological order: Before surgery, after surgery showing residual tumor, 4 years after surgery demonstrating progression of the disease, at the beginning of Doxorubicin regimen treatment, just after treatment discontinuation confirming <50% decrease in tumor size, and last follow-up 15 months after treatment discontinuation demonstrating a stable disease. Note the cystic component. (B) Sagittal after gadolinium injection T1-weighted imaging revealed dominant, patchy intense enhancing lesion of the splenium of the corpus callosum and the pineal region before surgery, after surgery, 4 years after surgery, at the beginning of Doxorubicin treatment, after treatment, and at last follow-up. (C) Axial FLAIR T2-weighted images revealing peritumoral edema by large heterogeneous hyperintense signal before treatment with Doxorubicin and at last follow-up. (D) Diagram of evolution of tumor volume on MRI revealed a decrease during and after the Doxorubicin period (grey).