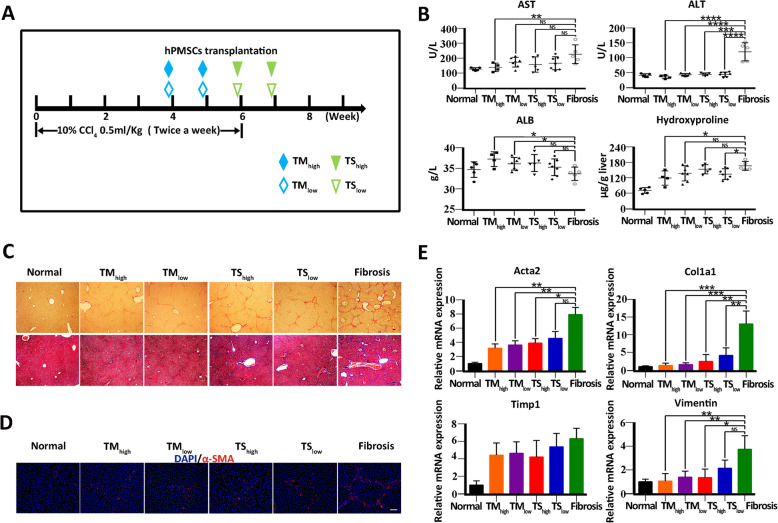
Fig. 1.
Therapeutic effects of hPMSCs in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. a Experimental scheme of hPMSC transplantation in CCl4-injured liver fibrosis. Intravenous injection of hPMSCs was administered. TMhigh, treatment with a high dose of hPMSCs in the mild-to-moderate stage of LF; TMlow, treatment with a low dose of hPMSCs in the mild-to-moderate stage of LF; TShigh, treatment with a high dose of hPMSCs in the severe stage of LF; TSlow, treatment with a low dose of hPMSCs in the severe stage of LF. A high dose was specified as 5 107 cells/kg and a low dose was specified as 2 107 cells/kg. b Hepatic function was assessed by serum level of AST, ALT, ALB, and hepatic hydroxyproline content in liver tissues in CCl4-injured mice that treated with or without hPMSCs. c Photomicrographs of liver sections stained with Sirius red (upper) and Masson trichome (bottom) at week 8. d Immunohistochemical staining using anti--SMA (red) and DAPI (blue) at week 8. e Expression of Acta2, Col1a1, Timp1, and Vimentin was determined using qRT-PCR. Relative mRNA expression was normalized to -actin and compared with the fibrosis group. Mice from fibrosis group received PBS followed by CCl4 injection. Scale bar, 50 m. ****p < 0.0001, ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05; ns, no significance, hPMSCs, human placental mesenchymal stem cells. TMhigh mice, n = 4/group; normal, TShigh, and Fibrosis mice, n = 5/group; TMlow and TSlow mice, n = 7/group