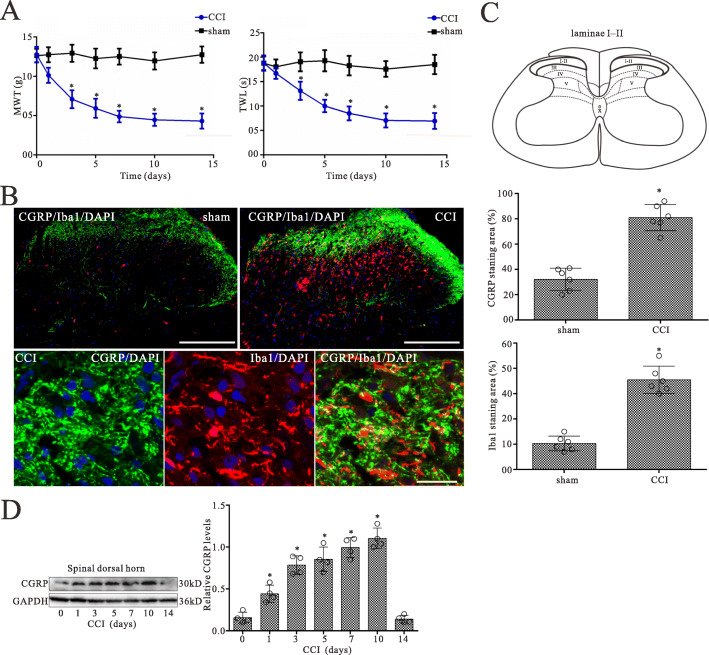
Fig. 1.
CCI evokes increases in the expressions of CGRP and Iba1 in the L4L5 spinal dorsal horn of CCI rats. a Nociceptive behavior developed in CCI model rats. Mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) and thermal withdrawal latency (TWL) were examined at 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 days respectively after sham operation or CCI surgery. n = 6, *p < 0.05 vs. sham group. b Double-staining immunofluorescent images showing the CGRP-positive fibers (green) and Iba1 (microglia maker)-positive microglia (red) in the dorsal horn of sham and CCI groups on day 5 after surgery. Cell nuclei were stained with the DAPI (blue). Note that numerous varicose nerve terminals immunoreactive for CGRP (green) closely approached and surrounded Iba1 immunopositive microglia (red) in the laminae I and II of the spinal dorsal horn (second row). Scale bar of 200 m in the first row and 10 m in the second row. c Quantitative analysis of the percentages of CGRP-immunoreactive surface in laminae I and II, and Iba1-immunostaining surface in the spinal dorsal horn showed the CCI-induced changes. Data are presented as the mean SEM (n = 6). *p < 0.05 vs. sham group. d Western blot analysis of CGRP expression in the spinal dorsal horn on 0, 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, and 14 days after CCI surgery, respectively. The mean optic density of the protein was calculated by normalizing to GAPDH. All values are expressed as the means SEMs (n = 4).*p < 0.05 vs. sham group