Figure 5: ERK1/2 inhibitor promotes stability of LPS-activated HMVEC monolayers.
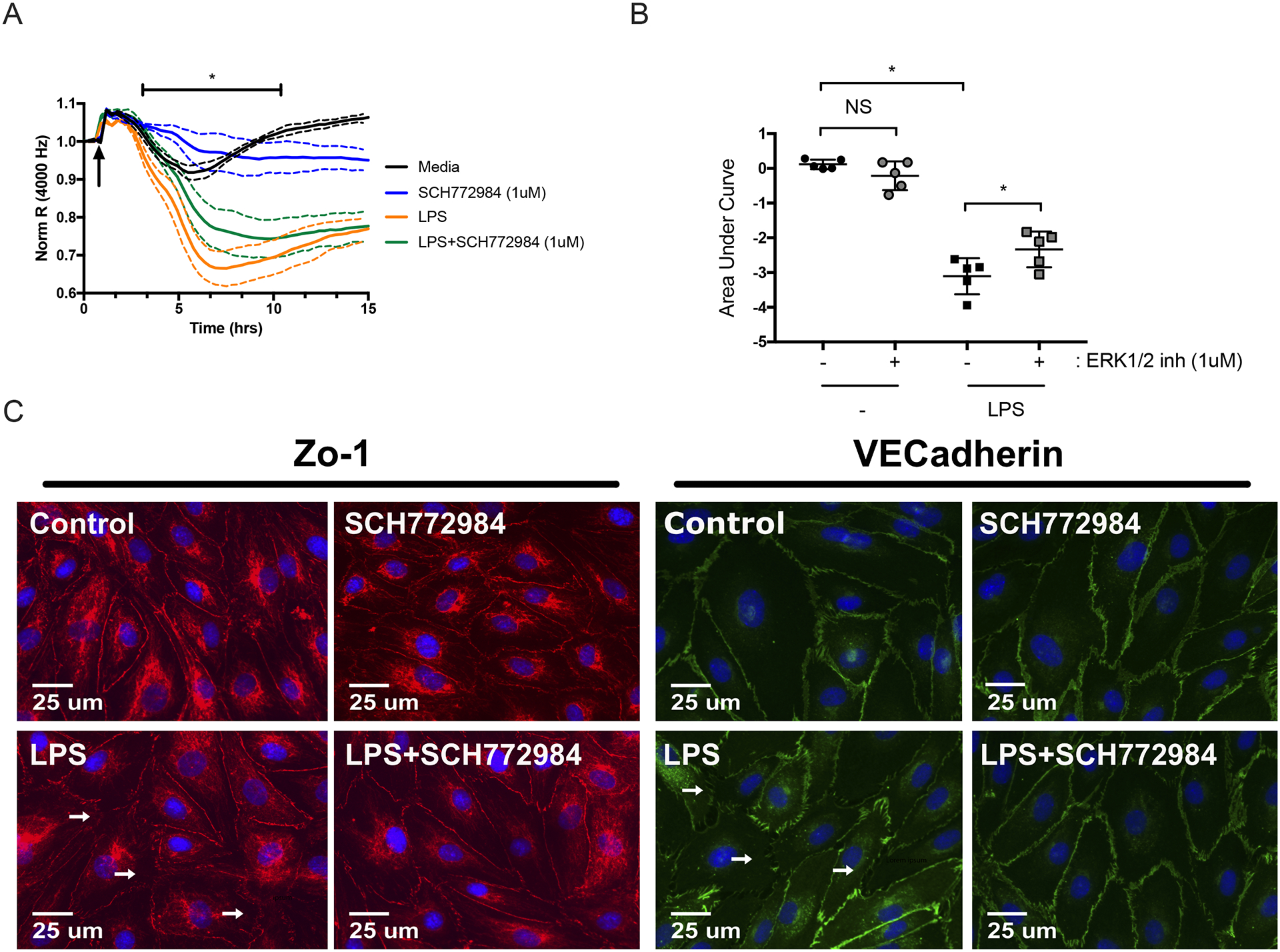
(A) ECIS was used to assess the effects of ERK1/2 inhibitor on LPS-induced HMVEC permeability. Cells were treated with LPS (1 μg/ml) in the continued presence of ERK1/2 inhibitor (1 μM) or vehicle. Data was normalized to the resistance immediately before the addition of LPS (arrow). (B) Area under the curve was then quantified from baseline = 1 with addition of negative peaks and graphed as means ± SD. Data was analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). n = 5; *p≤0.05; NS, not significant. (C) Representative fluorescence microscopy images of HMVEC treated with LPS (1 μg/ml) in the presence and absence of ERK1/2 inhibitor. Images were taken at 40x magnification. ZO-1(red), VEcadherin (green), or nuclei (blue). White arrows indicate examples of disrupted cellular junctions. Scale bar = 25 μm.
