Fig. 6. Endothelial-specific MAP4K4 KD vitiates MYDGF-mediated protection of endothelial injury in vivo.
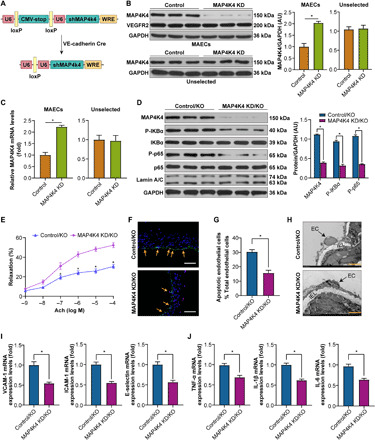
MAP4K4 KD/KO and control/KO mice were fed a WD for 12 weeks, and endothelial injury and NF-κB signaling were investigated. (A) Schematic of the transgenic construct used to generate MAP4K4 KD animals. (B and C) MAECs were derived from MAP4K4 KD and control mice. (B) MAP4K4 and VEGFR2 (vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2) protein expression in MAECs and unselected cell lysates (n = 3). (C) mRNA levels of MAP4K4 in immune-selected or unselected cells (n = 3). (U6, promoter; WRE, woodchuck hepatitis virus posttranscriptional regulatory element). (D) The expression levels of NF-κB signaling in MAECs of MAP4K4 KD/KO and control/KO mice (n = 6). Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) was used as a loading control. (E) The aortic vasodilatation induced by Ach in MAP4K4 KD/KO and control/KO mice (n = 10). (F) Representative images of TUNEL staining in sections of thoracic aortas. (G) The percentage of apoptotic endothelial cells (n = 6). (H) Representative electron microscopy images of endothelium. Scale bars, 50 μm. (I) The mRNA levels of adhesion molecules and (J) inflammation in MAECs of aortas (n = 10). The data are shown as the means ± SEM. *P < 0.001.
