Fig. 1. Soft phonons from inelastic neutron scattering.
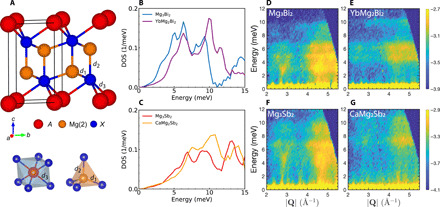
(A) Crystal structure of AMg2X2 and illustration of octahedral A-site and tetrahedral Mg(2) atoms. Red, orange, and blue represent A, Mg(2), and X, respectively. d1 and d2 are the nearest- and second-nearest-neighbor Mg(2)-X bonds. The nearest-neighbor A-X bond is d3. Comparison of experimental neutron DOS Ei = 20 meV at 300 K of (B) Mg3Bi2 (blue) and YbMg2Bi2 (purple) and (C) Mg3Sb2 (red) and CaMg2Sb2 (orange). Significant stiffening is observed in ternary compounds despite a heavier mass of Ca or Yb than Mg. Extra shoulders at low energy are observed only in binary compounds. Neutron dynamical structure factor S(∣Q∣, ω) of (D) Mg3Bi2, (E) YbMg2Bi2, (F) Mg3Sb2, and (G) CaMg2Sb2, the same datasets as in (B) and (C). Total intensities are normalized to the value of Mg3Bi2. Much stronger intensities at the low-energy region can be observed in binary compared to ternary compounds.
