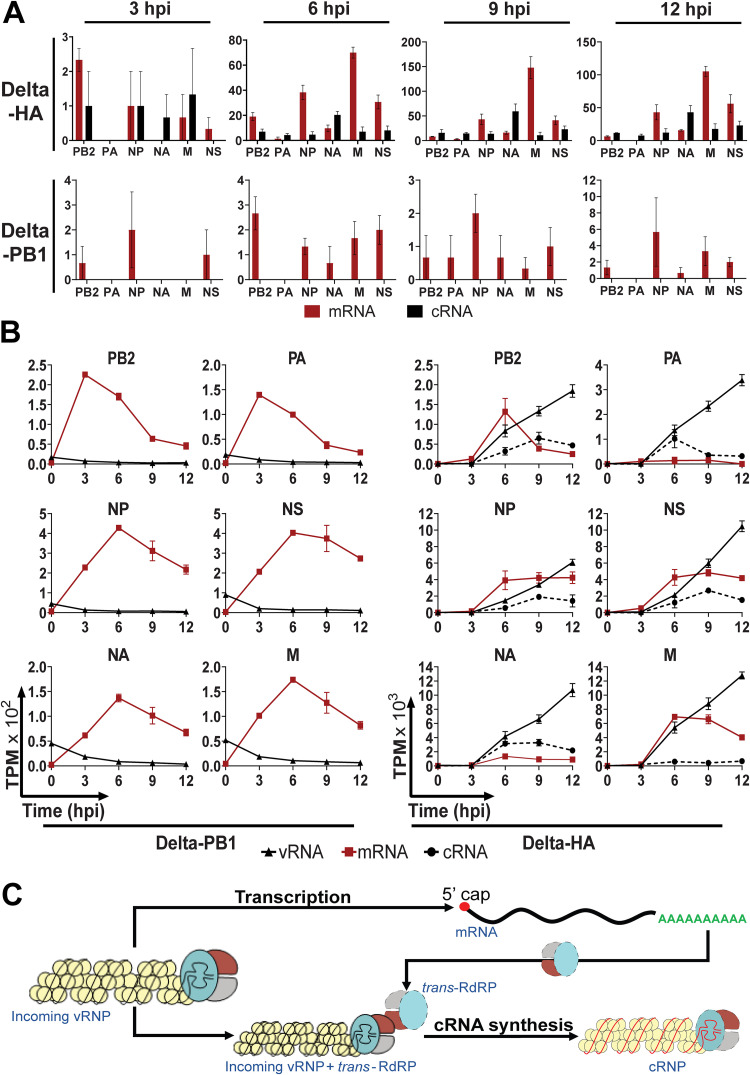
FIG 6.
Kinetics of delta-PB1 virus demonstrates that incoming polymerase cannot initiate cRNA synthesis. (A) Number of RNA-Seq read counts mapped to cRNAs versus mRNAs at the 3′ end. Number of RNA-Seq reads at the 3′ end that are differentiated into cRNA (black) or mRNA (red) reads from delta-HA virus (top row) and delta-PB1 virus (bottom row). Error bar indicates standard error of the mean (SEM). (B) Comparison replication kinetics of delta-HA and delta-PB1 viruses. Each panel in this trellis graph shows the kinetics of vRNA (▴), cRNA (●), mRNA (▪) of one viral segment along with time postinfection. Each graph plotted the average value of the three infections. Error bar indicates SEM. (C) Model for cRNA synthesis initiation. Incoming viral ribonucleoproteins (vRNPs) can initiate primary transcription to make mRNA for new RdRP protein. These newly synthesize RdRPs (trans-RdRPs) play roles in activating cRNA synthesis, potentially through the same trans-activating mechanism as in vRNA synthesis (3).