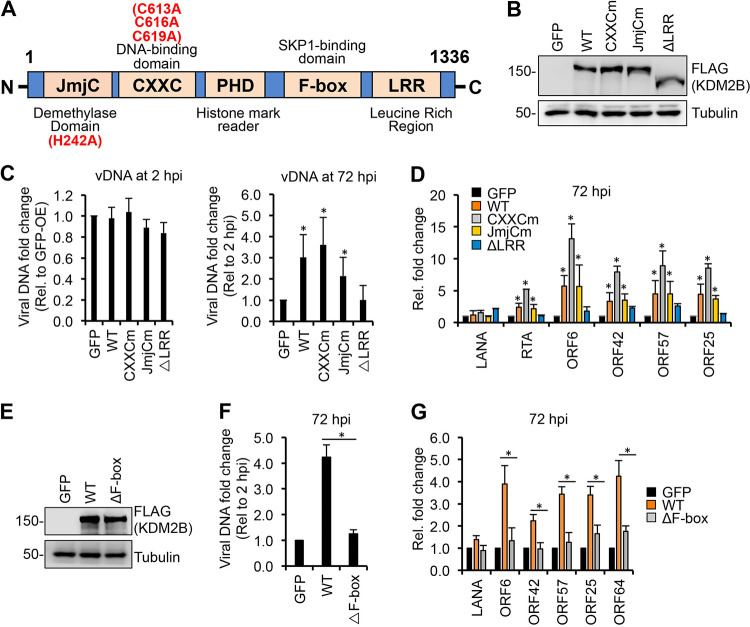
FIG 4.
Identifying the KDM2B domains required for KDM2B-mediated lytic gene expression. (A) Schematic representation of the domain structure of KDM2B. JmjC, Jumonji C histone demethylase domain; CXXC, DNA-binding domain; PHD, histone mark reader plant homeodomain; F-box, SKP1-binding domain; LRR, leucine-rich repeat. Point mutations in JmjCm and CXXCm are indicated. (B) FLAG immunoblot analysis of the expression of WT and mutant 3×FLAG-KDM2B in SLK cells transduced with lenti-3×FLAG-KDM2B. (C to G) SLK cells were transduced with lenti-GFP or lenti-3×FLAG-KDM2Bs for 3 days, followed by infection with KSHV for 3 days. (C) qPCR measurement of viral DNA at 2 hpi relative to GFP-OE cells and at 72 hpi relative to 2 hpi. (D) RT-qPCR analysis of viral gene expression in KDM2B-OE cells relative to GFP-OE cells at 72 hpi. (E) Immunoblot analysis of WT and mutant 3×FLAG-KDM2B expression in SLK cells. (F) qPCR analysis of viral DNA load at 72 hpi relative to 2 hpi. (G) RT-qPCR of viral mRNAs in KDM2B-OE cells relative to GFP-OE cells at 72 hpi. t tests were performed between GFP-OE and KDM2B-OE samples (C and D) and between WT and ΔF-box samples (F and G), and P < 0.05 (*) was considered statistically significant.