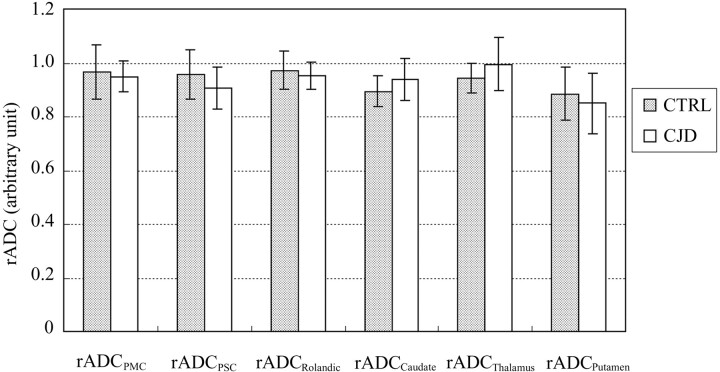
Fig 3.
rADC ratios between frontal (PMC) and parietal (PSC) Rolandic cortex ROI and commonly affected adjacent frontal (SFG) and parietal (SMG) lobe neocortical ROI in patients with CJD (white bars) do not differ significantly from the equivalent rADC ratios in control patients (shaded bars), confirming that gray matter diffusivity is abnormal to a similar degree in Rolandic cortex and other cortical areas in early CJD, despite apparent “sparing” of Rolandic cortex on DWI (Fig 1C). Likewise, rADC ratios in the deep nuclei do not differ between patients with CJD and control patients, suggesting that the degree of involvement of the caudate, putamen, and thalamus is similar to that of neocortex (individual P value range: 0.25–0.70).