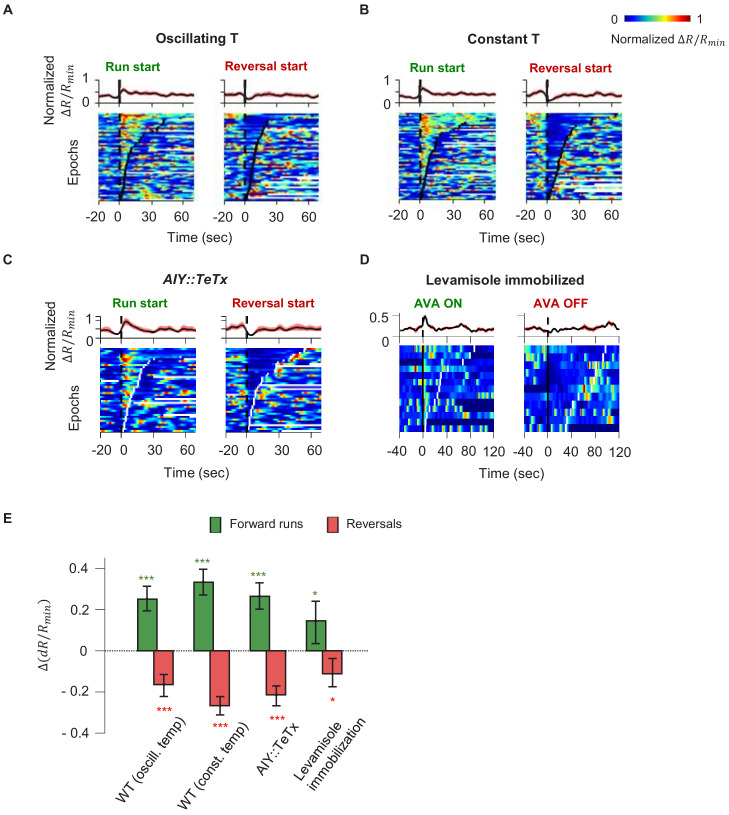
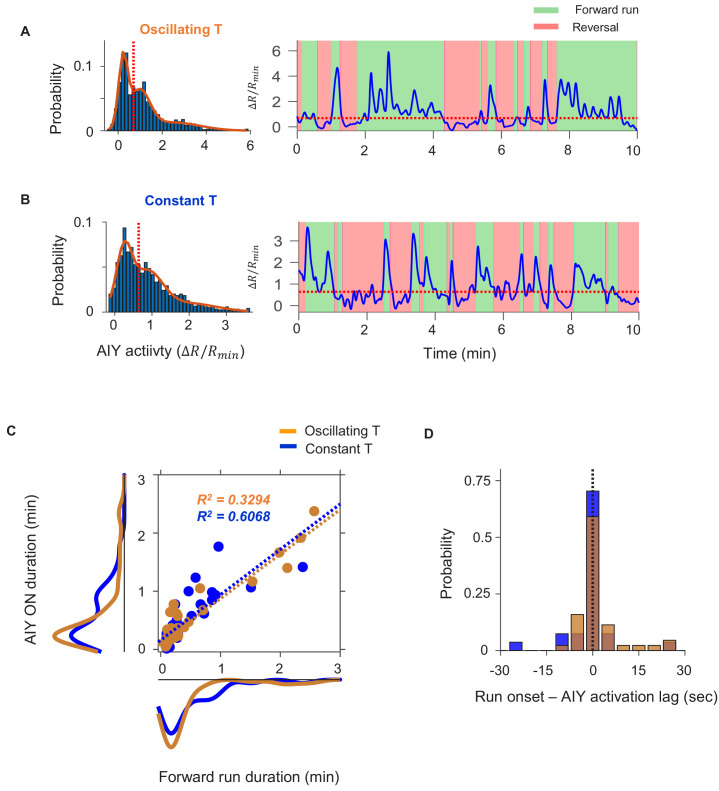
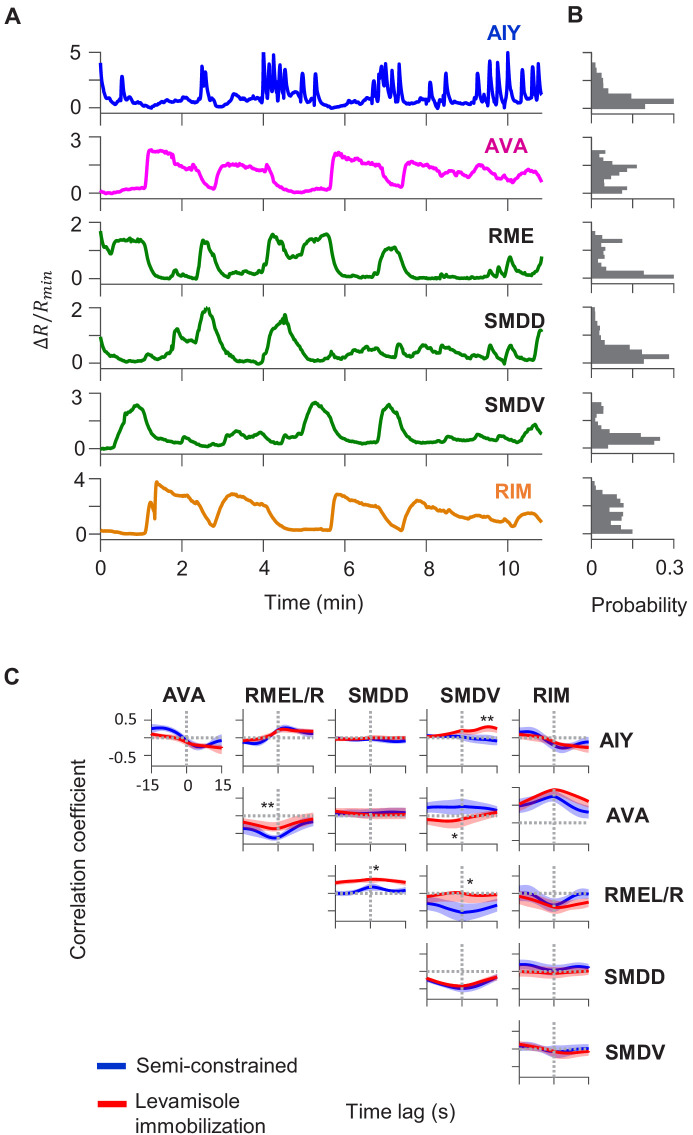
Figure 3. Motor-related activity in the AIY interneuron represents a corollary discharge signal.
(A, B) Calcium activity of the AIY interneuron aligned to the onset of forward runs (left column) or reversals (right column) in animals exposed to oscillating temperature (A, N = 6) or constant temperature (B, N = 5). Each row of the heat plots represents AIY calcium activity during a single behavioral epoch. The curve on top of each panel represents activity dynamics averaged across individual epochs. Broken lines indicate the onset and offset of each behavior epochs. (C) Calcium activity of the AIY interneuron aligned to the onset of forward runs or reversals in animals expressing tetanus toxin (TeTx) specifically in AIY (N = 4). (D) Calcium activity of AIY aligned to onset or offset of AVA activation in animals immobilized by the cholinergic agonist levamisole (N = 4). The ON and OFF states of AVA activity are defined by binarizing AVA activity using the Otsu method. See Materials and methods for details. (E) Change in AIY activity before versus. after the onset of forward runs (green) or reversals (red) for datasets shown in (A) and (B). Wilcoxon Signed rank test was used to test if the change in AIY activity has a median significantly different from zero, *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; n.s., non-significant.