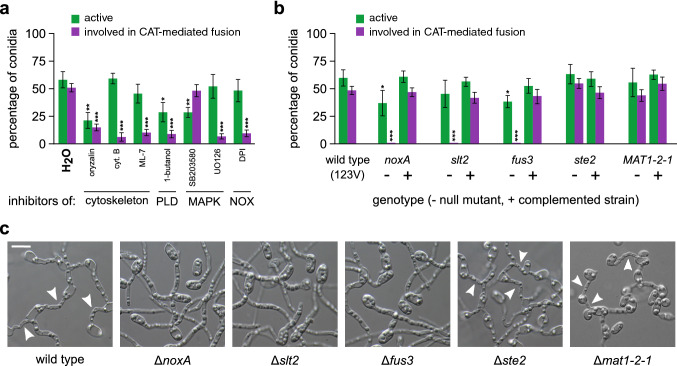
Fig. 5.
Somatic cell fusion in V. dahliae requires conserved signaling and cytoskeletal components. a Influence of inhibitors of cytoskeletal elements and the signaling components phospholipase D (PLD), MAP kinase cascades (MAPK), and ROS-generating NADPH complexes (NOX) on the frequencies of active conidia and active conidia involved in CAT-mediated fusion (isolate 123V). b Analysis of the fusion ability of V. dahliae 123V knock-out mutants for selected genes of NOX signaling (noxA), MAPK signaling (slt2, fus3 and ste2) and the mating-type gene (MAT1-2-1). Frequencies of active conidia and active conidia involved in CAT-mediated fusion are shown for each null mutant (–), in comparison to their corresponding rescued strains by complementation (+), and the wild type. Each inhibitor and mutant was tested in triplicate, and 300 conidia were analyzed per replicate. Bars = SD. Statistical significance of differences from the control (H2O or the wild type, respectively) was assessed using Student’s t-tests (*p ≤ 0.05, **p ≤ 0.01, ***p ≤ 0.001). c Fusion ability of the null mutants in comparison to their wild-type strain (V. dahliae 123V)