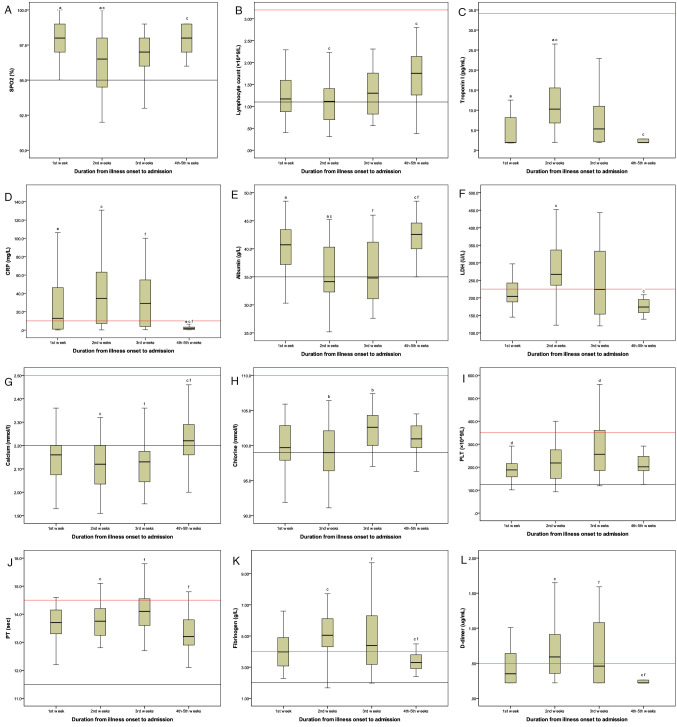
Figure 1.
Dynamic profiles of clinical signs over time in non-severe patients with COVID-19. In the first week after symptoms onset, COVID-19 patients showed remarkably decreased levels of lymphocyte count and calcium and slightly increased levels of C-reactive protein, lactic dehydrogenase, fibrinogen, and D-dimer. Meanwhile, the levels of albumin, high sensitive troponin I, and pulse oximeter O2 saturation remained unchanged. All the clinical signs, including lymphocyte count, electrolyte, albumin, high sensitive troponin I, C-reactive protein, lactic dehydrogenase, fibrinogen, D-dimer, and pulse oximeter O2 saturation, were at the peak (bottom) in the second week after symptoms onset. The majority of clinical signs improved in the third week, whereas C-reactive protein, lactic dehydrogenase, fibrinogen, and D-dimer were still at a relatively high level. All the above indicators were maintained at a significantly low (high) level during the fourth week to the fifth week after symptoms onset. Upper limit of reference interval (red line); Lower limit of reference interval (black line). SPO2 pulse oximeter O2 saturation, PLT platelet count, CRP C-reactive protein, LDH lactic dehydrogenase, PT prothrombin time.