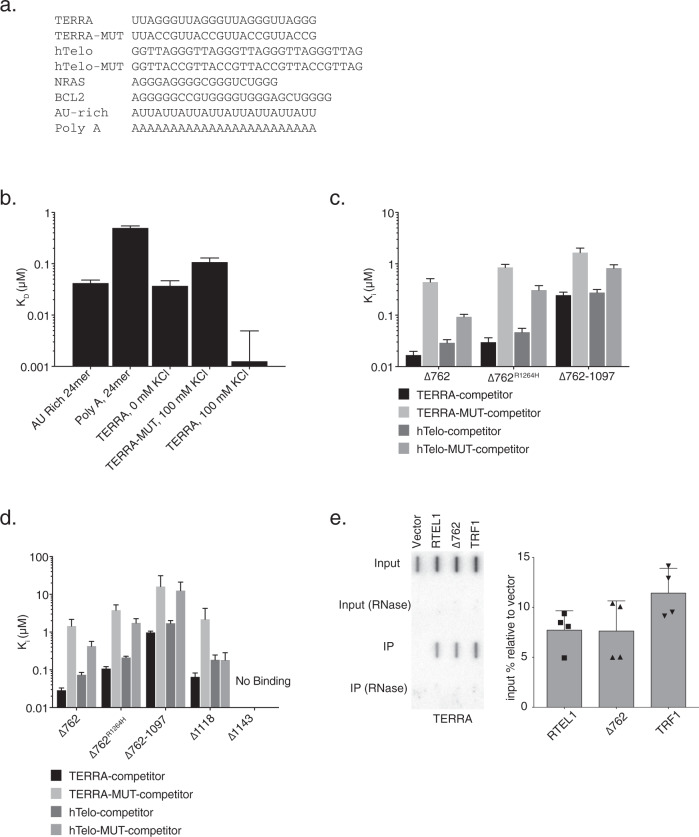
Fig. 2. The RTEL1 C-terminal Domain Binds TERRA and other G-quadruplex Structures.
a Sequences of DNA and RNA substrates used in this study. b Nucleic acid binding of RTEL1 proteins lacking the helicase domains was monitored by fluorescence anisotropy. Bar graph shows dissociation constants (KD) for TERRA and TERRA-MUT RNAs folded in the presence and absence of KCl and, AU-rich, and polyA RNA controls. c Increasing concentrations of the indicated oligonucleotides were added to reactions containing RTEL1 proteins and a 24mer FAM-TERRA-MUT RNA at 200 nM. Bar graphs depict apparent dissociation constants (Ki) derived by competition of the bound FAM-TERRA-MUT by the indicated oligonucleotides using fluorescence anisotropy. d Ki’s of the indicated RTEL1 deletion constructs were derived by competition studies of FAM-TERRA-MUT and indicated RTEL1 proteins at 1 µM as in panel C. No binding signal was observed for the RTEL1∆1143 protein. All binding assays were conducted in triplicate, mean and standard deviation are shown. e RNA IP assays were done in HEK293T cells transfected with FLAG-tagged RTEL1, ∆762, TRF1 or vector only control. Precipitated nucleic acids were treated with DNAse I for 1 h at 37 °C. IP RNA was analyzed by slot blotting and detected by autoradiography using a telomeric probe. Quantitation of four independent experiments with the mean and standard deviation of relative RNA-IP normalized to the vector only control is shown. Five percent of the input is shown in the top two rows. RNAse treatment is indicated (see also Supplementary Figs. 2–7).