Fig. 2.
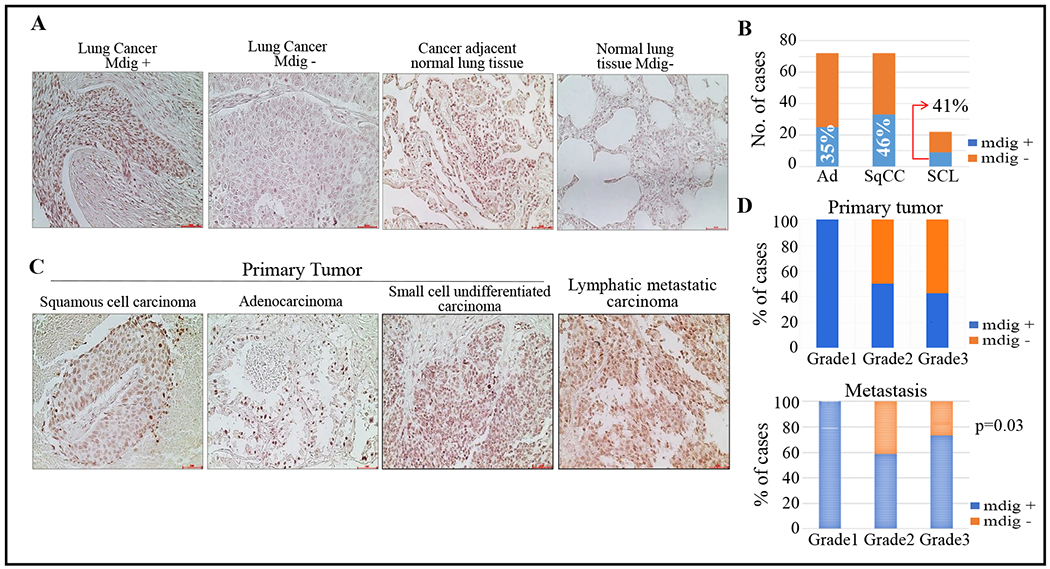
mdig expression in lung cancer with matched lymph node metastasis. (A) Immunohistochemistry of lung cancer tissue microarray stained for mdig protein. Lung cancer tissue microarray slide LC2085c was used, which contains normal lung tissue, cancer-adjacent normal tissue, and 168 cases of multiple types of lung cancer (grade 1-3), 10 each of normal and cancer-adjacent normal tissue with a single core of cancer and duplicated cores of normal or cancer-adjacent normal tissue. Regions of lung cancer showing both mdig-positive and -negative signal, mdig was absent from the normal lung tissues. Magnification 20× and scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Display of the mdig staining quantification and summary. (C) Immunohistochemistry of lung cancer tissue microarray with matched metastatic lymph nodes stained for mdig protein. Tissue array slide LC817a was used in this analysis. This slide contains 17 cases of lung SqCC, 17 cases of lung Ad, and 6 cases of lung small cell carcinoma, with duplicate cores per case. Each case was matched with lymph node metastatic tissues. Regions of lung cancer showing both mdig-positive and -negative signal. Magnification20× and scale bar = 50 μm. (D) mdig staining quantification in primary tumor and matched metastatic lymph nodes, additionally showing the mdig positivity with tumor grade as one of the parameters in the current analysis.
