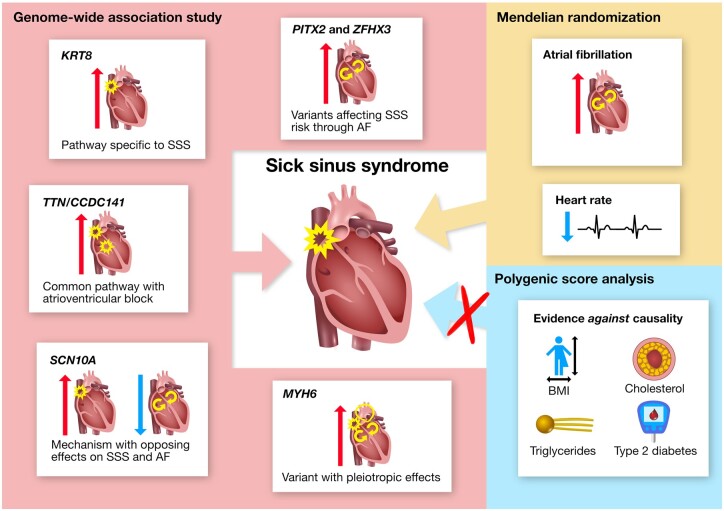
Summary of genetic insight into the pathogenesis of SSS and the role of risk factors in its development. Variants at six loci (named by corresponding gene names) were identified through GWAS and their unique phenotypic associations provide insight into distinct pathways underlying SSS. Investigation of the role of risk factors in SSS development supported a causal role for AF and heart rate and provided convincing evidence against causality for BMI, cholesterol (HDL and non-HDL), triglycerides and T2D. Mendelian randomization did not support causality for CAD, ischaemic stroke, heart failure, PR interval or QRS duration (not shown in figure). Red and blue arrows represent positive and negative associations, respectively.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.