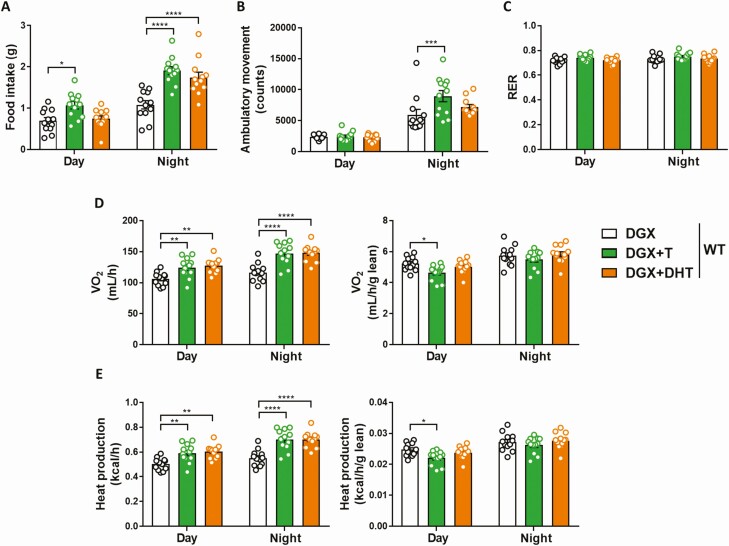
Figure 3.
Effect of T and DHT supplementation on physical activity and energy balance of HFD-fed chemically castrated male WT mice. Food intake (A), ambulatory movement (B), respiratory exchange ratio (C), oxygen consumption (D), and heat production (E) as measured by indirect calorimetry in 32- to 36-week-old male WT mice injected with degarelix, supplemented with placebo (DGX), T (DGX + T), or dihydrotestosterone (DGX + DHT) and subjected to HFD from 16 weeks of age (n = 12/group). D, E (right panels): Oxygen consumption and heat production were normalized to lean body mass. Data were analyzed with two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Abbreviations: ANOVA; analysis of variance;DGX, degarelix; DHT, dihydrotestosterone; HFD, high fat diet; RER, respiratory exchange ratio; SEM, standard error of the mean; T, testosterone; VO2, oxygen consumption; WT, wild type.