Figure 4.
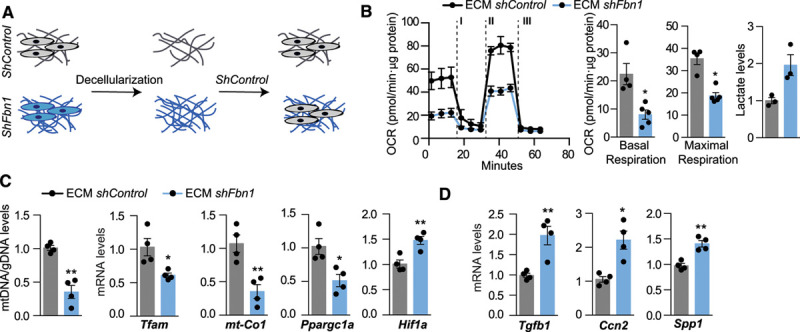
ECM derived from thoracic aortic aneurysm cells decreases Tfam levels and mitochondrial respiration. A, Primary vascular smooth muscle cells transduced with shFbn1 or shControl were cultured for 5 days, lead to produce ECM, then the matrices were decellularized and shControl cells were seeded. B, OCR in shControl vascular smooth muscle cells seeded in shControl and ShFbn1-ECM at basal respiration and after addition of oligomycin (I) and fluoro carbonyl cyanide phenylhydrazone (II) to measure maximal respiration, followed by a combination of rotenone and antimycin A (III) and extracellular lactate levels. C, Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis of Tfam, Mt-co1, Ppargc1, and Hif1a, and quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis of mtDNA content. D, Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis of synthetic genes Tgfb1, Ccn2, and Spp1. Statistical significance was assessed by Student t test. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs Control. Ccn2 indicates cellular communication network factor 2; ECM, extracellular matrix; Hif1a, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 α; mt-Co1, mitochondrially-encoded cytochrome c oxidase I; OCR, oxygen consumption rate; Ppargc1, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1; shFbn1, Short hairpin RNA Fbn1; Spp1, secreted phosphoprotein 1; Tfam, mitochondrial transcription factor A; and Tgfb1, transforming growth factor β1;
