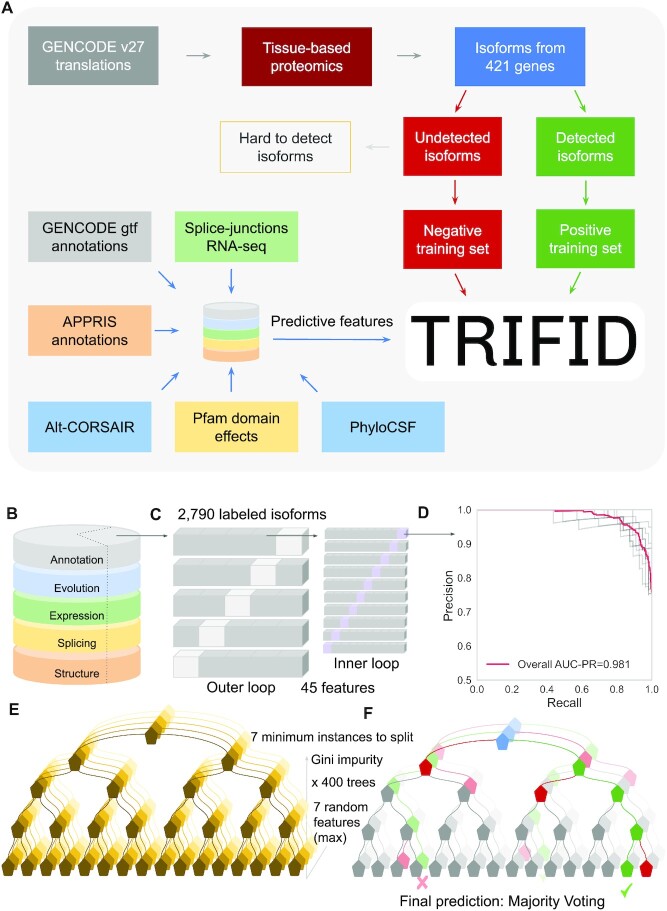
Figure 1.
Schema and model selection, training and feature importance in the final RF model. (A) A simplified schema of the design of the TRIFID algorithm. (B) Isoforms in the training set were annotated with features. (C) Nested cross validation (CV) strategy using an external test set to evaluate the performance of the model (to overcome the risk of test set bias). (D) Precision-recall curves from stratified 10-fold cross validation for the best model selected in the inner loop (75% of the training set, 2062 isoforms) once the hyperparameter tuning step has been performed. (E) Graphical representation of the RF training process. The RF had 400 de-correlated decision trees, and the best split of each tree was based on the Gini impurity function. At each leaf node, the minimum number of samples was set to 7, which also helps to avoid overfitting. (F) The predicted functionality score of an input isoform is the average predicted class probabilities of the trees in the forest.