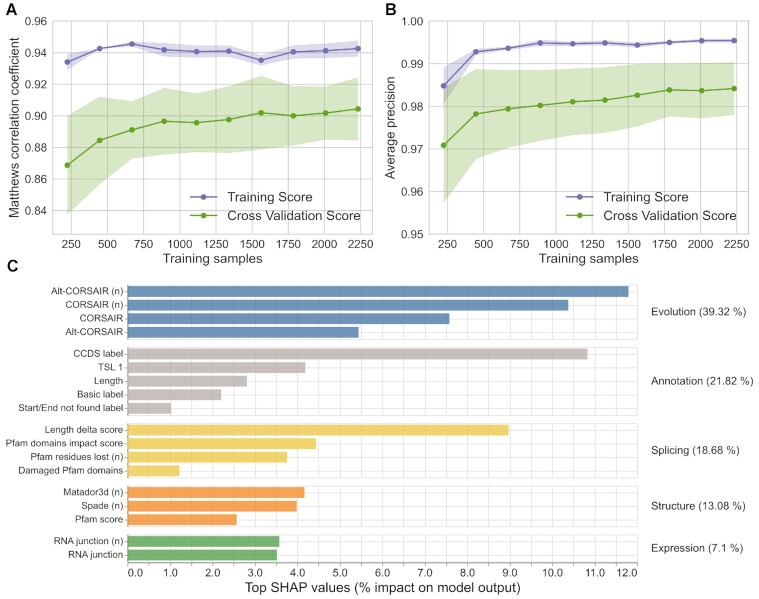
Figure 2.
TRIFID learning curve and feature importance. The Matthews correlation coefficient (A) and the average precision (B) for the training score and cross-validation score using subsets of the data set to train the model. Results clearly show that the model is stable even with smaller subsets. (C) The SHAP feature importance calculation (60) is a game theoretic approach that explains models globally by combining local contributions of individual features and is supposed to perform better than any other global approximation. The top 18 features are divided into five sub-types (evolutionary, annotation, structure/functional, expression and splicing effects) as described in the methods section. A lower case ‘n’ indicates that the feature was normalized.