Figure 5.
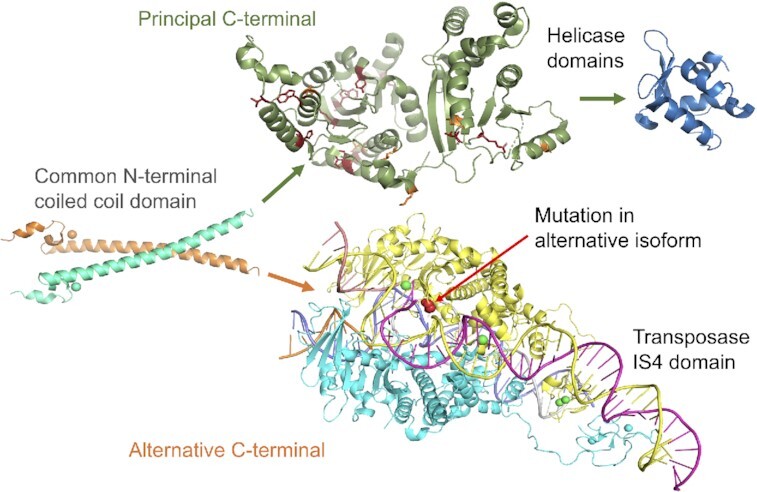
A schematic illustration of the two functionally important ERCC6 isoforms. Both isoforms have a common N-terminal, represented by the resolved coiled coil structure of residues 84 to 160 from PDB (73) structure 4CVO, left. The principal isoform (above right, red arrows) is represented by structures of the SNF2 family N-terminal domain (PDB: 5HZR) and C-terminal helicase domain (PDB: 6A6I). Pathogenic mutations from ClinVar (74) that map to the N-terminal domain are shown in red (stop gained) and yellow (missense). The alternative isoform (below right, blue arrows) is represented by the structure of the transposase IS4 domain (PDB: 6×67). The pathogenic mutation that affects ovary function (72) is mapped to this domain and shown in red. Mapping to the PDB structures where necessary was carried out using HHPRED (75) and all images were generated using PyMol.
