Table 2.
The clinical applications and the biofilm inhibition efficacy of 14 major classes of NO donors. A, approved drugs, drugs that have been officially accepted for commercialization in at least one jurisdiction at a given time. I, investigational drugs, which are being researched for a determinate condition and have reached clinical trials. E, experimental drug (drug in discovery or prediscovery phase). These drugs are being actively pursued but have not entered clinical trials. They exhibit drug-like properties but have not been formally considered as a drug candidate. Information on A, I, and E stages of drugs is obtained from DrugBank. "Disperse" refers to (I) a transition from sessile biofilm cells to motile planktonic cells, where the CFU of remaining biofilms is decreased, and the planktonic cells in the culture medium/flow cell effluent are increased proportionally; (II) a reduction of biomass/biovolume in the remaining biofilms as indicated by microscope/crystal violet staining/CFU counts. "Inhibit" refers to a prevention of biofilm formation on the surfaces, measured by microscope/crystal violet staining/CFU counts
| Class | Representative compounds | FDA category | Efficacy against biofilms? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrates | Nitroglycerin | A, I | Yes, inhibit S. aureus biofilms (Abbas et al. 2019) |
| Isosorbide dinitrate | A, I | unknown | |
| Isosorbide mononitrate | A | Yes, disperse S. aureus biofilms (Hasan et al. 2018; Jardeleza et al. 2014; Zhang et al. 2019b) | |
| Erythrityl tetranitrate | A, E, I | unknown | |
| Pentaerythritol tetranitrate | A | unknown | |
| Isosorbide | A, I | Inhibit dental biofilms (Beauté by Roquette® PO 500) | |
| Propatyl nitrate | E, I | unknown | |
| Methylpropylpropanediol dinitrate | E | unknown | |
| Tenitramine | E | unknown | |
| Trolnitrate | E | unknown | |
| Nitrate | E, I | Yes, inhibit Burkholderia pseudomallei biofilms (Mangalea et al. 2017) | |
| Nitrite | Amyl nitrite | A | Unknown |
| Sodium nitrite | A, I | Yes, kill/inhibit P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, B. cepacia, S. epidermidis, K. pneumoniae and Enterobacter cloace biofilms (Major et al. 2010; Zemke et al. 2014; Schlag et al. 2007; Kishikawa et al. 2013) | |
| isobutyl nitrite | A | Unknown | |
| Metal-NO complexes | Nitroprusside | A | Yes, inhibit/disperse P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, B.cepacia, E.coli, N. gonorrheae and S. epidermidis biofilms (Barraud et al. 2009a, b) |
| Diazeniumdiolates (NONOates) | Spermine NONOate | E, animal models (Li et al. 2020), promising anti-cancer drug | Yes, inhibit/disperse P. aeruginosa biofilms (Cai and Webb 2020) |
| MAHMA NONOate | Yes, disperse P. aeruginosa, E.coli O157:H7 and Salmonella enterica biofilms (Barnes et al. 2013; Marvasi et al. 2014) | ||
| Proli-NONOate | Yes, disperse multispecies biofilms on reverse osmosis membranes (Barnes et al. 2015) | ||
| DEA-NONOate | Yes, disperse Salmonella enterica biofilms (Marvasi et al. 2014) | ||
| DETA-NONOate | Yes, disperse S. aureus (Jardeleza et al. 2011) and multispecies biofilm on biofouled membranes (Oh et al. 2018) | ||
| DPTA-NONOate | Yes, disperse P. aeruginosa biofilms co-cultured with epithelium cells (Zemke et al. 2020) | ||
| PAPA-NONOate | Yes, disperse multispecies biofilm on biofouled membranes (Oh et al. 2018) | ||
| Nitrosothiol | SNAP (S-Nitroso-N-acetyl-d,1-penicillamine) | E | Yes, disperse P. aeruginosa (Barraud et al. 2006), S. enterica, pathogenic E. coli and Listeria innocua biofilms (Marvasi et al. 2016) |
| SNVP (S-Nitroso-N-valeryl penicillamine) | E (isolated femoral arteries from rat)(Miller et al. 2000) | unknown | |
| GSNO (S-nitroso-glutathione) | Clinical trial (Liu et al. 2020) | Yes, disperse/kill/inhibit P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii and S. aureus biofilm (surface/nanoparticle) (Barraud et al. 2006; Lee et al. 2020; Paricio et al. 2019) | |
| SNOC (S-Nitrosocysteine) | E (animal model, potent anti-platelet agent) (Stuesse et al. 2001) | unknown | |
| SNAC (S-Nitroso-N-acetyl-cysteine) | E (animal model) (De Oliveira et al. 2006) | unknown | |
| HomocysNO (S-Nitrosohomocysteine) | E (animal model) (Jansen et al. 1992) | unknown | |
| RIG200 | E (animal model and clinical trials) (Megson et al. 1997; Sogo et al. 2000) | unknown | |
| Furoxan derivatives | Ipramidil | E (isolated guinea pig working heart) (Feelisch et al. 1992) | unknown |
| 4-methyl-3-phenyl sulfonylfuroxan | E (Ghigo et al. 1992) | unknown | |
| C92-4609 (4-hydroxymethyl-furoxan-3-carboxamide, CAS 1609) | E (isolated rabbit femoral artery and jugular vein) (Hecker et al. 1995) | Unknown | |
| C92-4678(4-phenyl-furoxan-3-carboxylic acid (pyridyl-3-yl-methyl)-amide) | unknown | ||
| C92-4679 (3-phenyl-furoxan-4-carboxylic acid (pyridyl-3-yl-methyl)-amide) | Unknown | ||
| C93-4759 (3-hydroxymethyl-furoxan-4-carboxamide) | unknown | ||
| 4-(phenylsulfonyl)-3-{[(2-dimethylamino)ethyl]thio}furoxan) | NA | Yes, disperse P. aeruginosa biofilm (Poh et al. 2017) | |
| 3-formyl-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole N2-oxide and 3-carbonitrile-4-phenyl-1,2,5-oxadiazole N2-oxide | E (animal model, antitumor) (Aguirre et al. 2006) | unknown | |
| (E)-4-(4-((2-isonicotinoylhydrazono)methyl)phenoxy)-3-(phenylsulfonyl)-1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide (Novel furoxan derivative) | E (animal model against TB) (dos Santos Fernandes et al. 2016; de Souza et al. 2020) | unknown | |
| 20 water soluble furoxan derivatives | E (isolated thoracic aortas from rat) (Sorba et al. 1997) | unknown | |
| benzodifuroxan and benzotrifuroxan | E (C6 cells and isolated aorta strips from rat) (Medana et al. 1999) | unknown | |
| Sydnonimines | Molsidomine | Not approved by FDA but available in Europe (Kwon and Rosendorff 2018) | Yes, disperse S. enterica, E. coli O157:H7, L. innocua and Pectobacterium biofilms (Islam et al. 2020; Marvasi et al. 2014) |
| Linsidomine | E (clinical trial, patients with erectile dysfunction)(Stief et al. 1992; Truss et al. 1994) | unknown | |
| Pirsidomine | E (animal model, pig and dog) (Martorana et al. 1994; Wainwright and Martorana 1993) | unknown | |
| N-hydroxyguanidines | N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N′hydroxyguanidine | E | unknown |
| N-butyl-N′-hydroxyguanidine | E | unknown | |
| Hydroxyureas and derivatives | Hydroxyurea | A | Yes, induce P. aeruginosa biofilm through SOS stress response (Gotoh et al. 2010) |
| (R)-(+)-N-[3-[5-[(4-fluorophenyl)methyl]-2- thienyl]-1-methyl-2-propynyl]-N-hydroxyurea (ABT-761, Atreleuton) | I (clinical trials terminated at phase III)(Brooks et al. 1995; Reid 2001) | unknown | |
| Hydroxylamine and derivatives | N-methyl-hydroxylamine | NA | Yes, inhibit/disperse P. aeruginosa biofilms (Julián et al. 2015) |
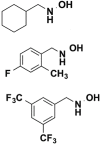 |
NA | Yes, inhibit/disperse P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and E. coli biofilms (Miret-Casals et al. 2018) | |
| Oximes | cyclohexanone oxime | Hematotoxic in rats (Derelanko et al. 1985; Glover et al. 1999) | unknown |
| 4-ethyl-2E-(hydroxyimino)-5-nitro-3E-hexenamide (FK-409) | E (rat aortic transplant model) (Fukada et al. 2000; Zhang et al. 2000) | unknown | |
| 1,2-diazetine 1,2-dioxides (DD) | 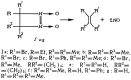 |
E (except for Ie, most DD derivatives reduce the spasm of isolated rat aorta and the arterial pressure in hypertensive rats) (Shvarts et al. 1994) | unknown |
| Oxatriazole-5-imine | GEA 3162 and GEA 3175 (mesoionic 3-aryl substituted oxatriazole-5-imine derivatives) (Kankaanranta et al. 1996; Karup et al. 1994) | E (rat neutrophils, rabbit aortic endothelial cells, isolated pig trachea, rat bronchi and bovine and human small bronchioles) (Taylor et al. 2004; Laursen et al. 2006; Elmedal et al. 2005; Hsu et al. 2006; Malo-Ranta et al. 1994) | unknown |
| Heterocyclic N-Oxides | N–O moiety can elicit nitric oxide-like functions(Mfuh and Larionov 2015). Minoxidil,kopexil, N,N-diallylmelamine etc | Minoxidil is at A and I stage | unknown |
