Table 1.
The docking score and binding energy of the top five compounds docked against PfDegP within the allosteric pocket (S2).
| Structure | 2D Structure | Title | LF Rank Score 1 | LF dG 2 | LF vs. Score 3 | MW 4 | Atoms | SlogP 5 | TPSA 6 | RB 7 | Rof5 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [O-][N+](=O)c1cc([N+]([O-])=O)ccc1NCCCC([O-])=O |
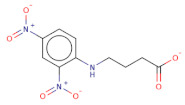
|
RJC02337 | −16.742 | −8.149 | −9.451 | 268.2 | 19 | 1.6 | 143.8 | 7 | 0 |
| O=C(N)c1cc([N+]([O-])=O)cc([N+]([O-])=O)c1C |
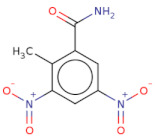
|
T0873 | −15.539 | −7.431 | −9.133 | 225.2 | 16 | 0.7 | 134.7 | 3 | 0 |
| O[C@@H]1[C@H](O[C@@H]([C@H](O)[C@@H]1O)CO)OC[C@@H]2[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](O2)OC(=O)/C(=C/C=C/C(C)=C/C=C/C=C(\C=C\C=C(\C(O[C@@H]3[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O3)CO[C@@H]4[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](O4)CO)=O)C)C)C |
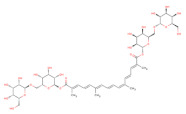
|
T2823 | −15.515 | −13.277 | −19.591 | 977 | 68 | −0.6 | 391.2 | 32 | 3 |
| [O-][N+](=O)c1cc2c(OC)cccc2c3c4c(OCO4)cc(c13)C([O-])=O |
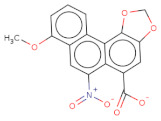
|
T2801 | −15.35 | −8.138 | −10.132 | 340.3 | 25 | 3.2 | 113.6 | 3 | 0 |
| [O-][N+](=O)c1c(cc(N/N=C/c2ccco2)c([N+]([O-])=O)c1)C |
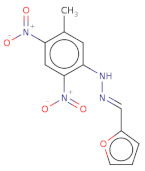
|
CD00811 | −15.321 | −7.022 | −9.005 | 290.2 | 21 | 2.1 | 129.2 | 5 | 0 |
| OP(OC(C)C)OC(C)C |
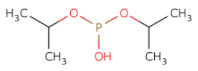
|
DFP | −9.916 | −5.191 | −5.268 | 165.1 | 10 | 2.5 | 35.5 | 4 | 0 |
1 This function is used for ranking ligand poses obtained during a docking run. The purpose of this function is to reproduce experimentally observed ligand poses as well as possible. 2 This scoring function has been designed to perform accurate estimation of the free energy of protein-ligand binding for a given protein-ligand complex. 3 This function has been designed to produce maximum efficiency in virtual screening experiments i.e., to assign higher scores to active ligands (true binders) and lower scores to inactive ligands. 4 Molecular weight. 5 Log of the octanol/water partition coefficient (including implicit hydrogens). 6 Polar surface area calculated using group contributions with the parameters of Ertl et al. (2000). 7 Rotatable bonds. 8 Lipinski’s rule of five.
