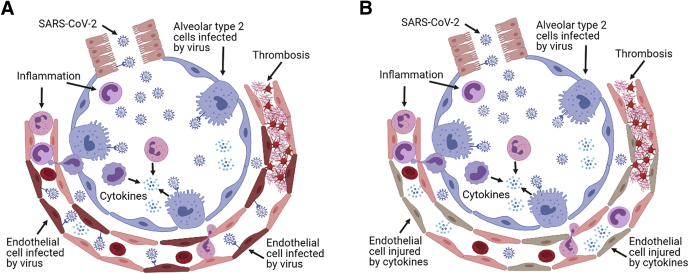
Figure 1.
Proposed causes of endothelial injury in coronavirus disease 2019 vasculopathy. A: Direct injury of the endothelium by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). B: Indirect injury of the endothelium by an excessive inflammatory reaction to the viral infection of alveolar and bronchiolar epithelial cells. The injured endothelium in both scenarios develops a proinflammatory phenotype and loses its antithrombogenic properties. The hypothesis that endothelial cells are directly injured by the virus has been challenged by recent studies reporting that endothelial cells do not express the angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 receptor or express it at low levels and are resistant to the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Image created with BioRender software (BioRender, San Francisco, CA).