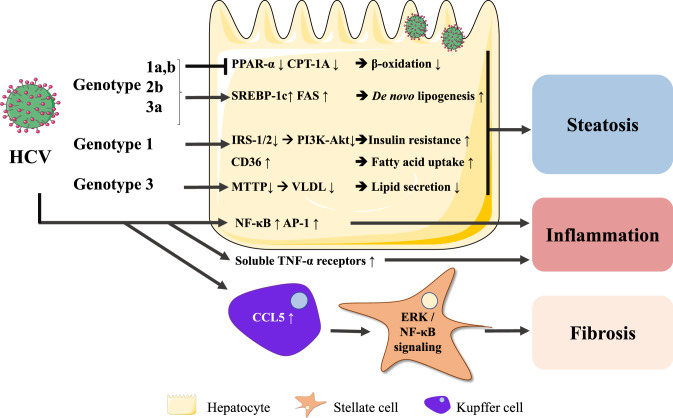
Fig. 2.
HCV-mediated mechanisms leading to hepatic steatosis and inflammation. HCV infection leads to SREBP-1c-mediated lipid accumulation and PPAR-α/PPARA and CPTA downregulation, suggesting impaired fatty acid β-oxidation and reduced repression of inflammation. HCV genotypes 1 and 4 infections are associated with insulin resistance, while HCV genotype 3 infection impairs VLDL-mediated triglyceride secretion. HCV-exposed Kupffer cells secrete CCL5 resulting in hepatic stellate cell activation