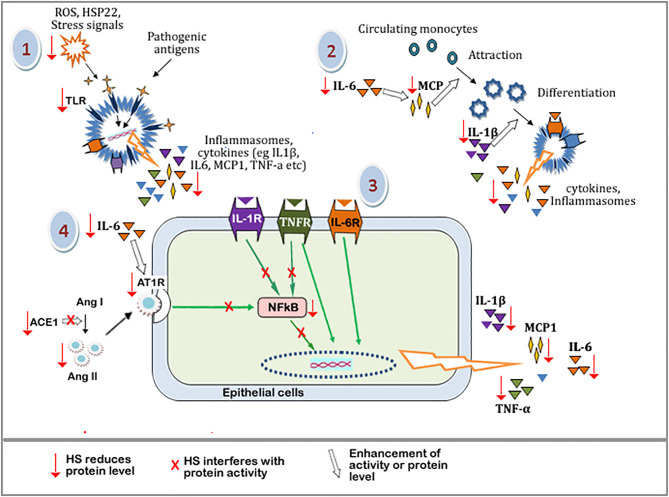
Figure 14.
Schematic diagram showing the tentative mechanism of HS anti-inflammatory activities. Oxidative stress and other cellular damage cause the activation of TLRs, which leads to the expression of inflammatory mediators. These mediators further perpetuate immune responses causing the release of more inflammatory mediators. HS interferes with various steps along these pathways (shown by red arrow). Steps with a red arrow indicate that HS reduced the level of the component of that step. Steps with a red “X” means that HS inhibited or interfered with the protein activity along that pathway. The white arrow means that the activity or level of a component is enhanced.\ TLRs, Toll-like receptors; ROS, Reactive oxygen species; HSP22, heat shock protein 22; IL-6, Interleukin 6; IL-1b, interleukin 1b; MCP-1, Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1; NFkB, Nuclear factor kappa B; IL-1R, Interleukin 1 receptor; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor; IL-6R, Interleukin 6 receptor; Ang I, Angiotensin I; Ang II, Angiotensin II; ACE-1, Angiotensin converting enzyme 1; AT-1R, Angiotensin II type 1 receptor.