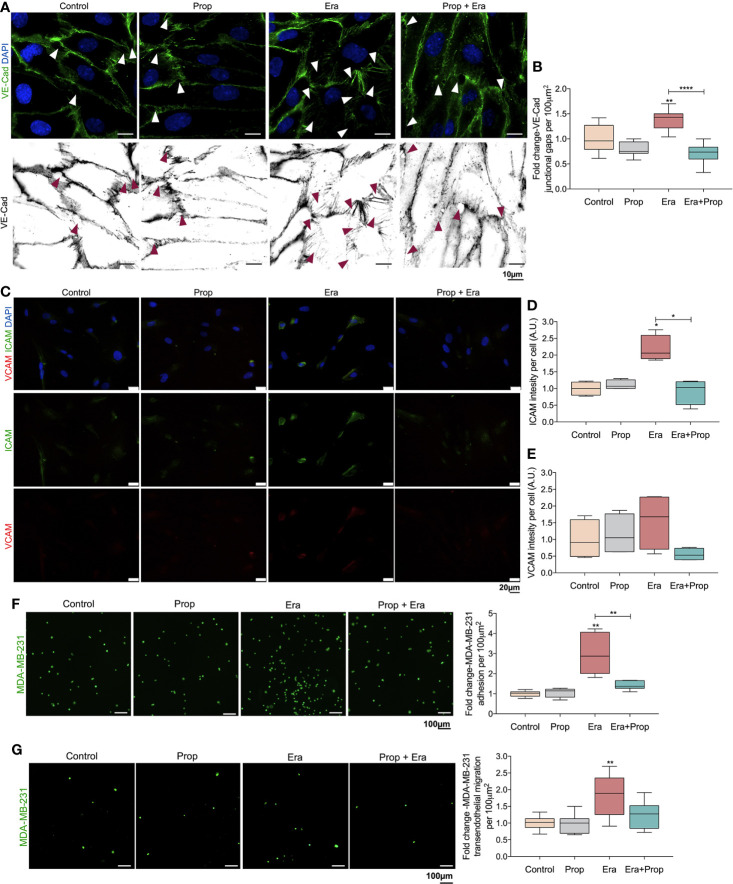
Figure 3.
Erastin (Era) promotes the generation of a leakier EC monolayer while increases cancer cell-EC interaction and transendothelial migration. (A) The ferroptosis-like mechanism driven by Era promotes an increased generation of intercellular VE-Cadherin (VE-Cad) gaps per 100µm2, while Propranolol (Prop) is able to revert this phenotype. The panel shows representative images (scale: 10 µm) of VE-Cadherin (green) intercellular junctional gaps (arrows) in HUVECs exposed to Era and/or Prop for 16h. (B) Quantification of VE-Cad junctional gaps. (C) Immunofluorescence for ICAM and VCAM detection. (D) ICAM intensity per cell (HUVECs; A.U.: arbitrary units) increases upon Era exposure and although Prop alone does not affect ICAM expression, it is able to abrogate the expression induced by Era, at 16h. (E) VCAM intensity per cell (A.U.: arbitrary units) shows a tendency to increase under Era exposure. The ferroptosis-like mechanism, induced by Era, promotes cancer cell (MDA-MB-231-calcein labelled cells) adhesion to HUVECs (F) and transendothelial migration (G). Prop alone has no effect but impairs cancer cell adhesion and transendothelial migration induced by Era. The panels show representative microscope images (scale: 100 µm; MDA-MB-231-calcein labelled cells (green)). All data are normalized to the control condition and represented as mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.